Human psychopharmacology and dose-effects of salvinorin A, a kappa opioid agonist hallucinogen present in the plant Salvia divinorum
- PMID: 21131142
- PMCID: PMC3089685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2010.11.005
Human psychopharmacology and dose-effects of salvinorin A, a kappa opioid agonist hallucinogen present in the plant Salvia divinorum
Abstract
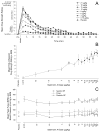
Salvinorin A is a potent, selective nonnitrogenous kappa opioid agonist and the known psychoactive constituent of Salvia divinorum, a member of the mint family that has been used for centuries by Mazatec shamans of Mexico for divination and spiritual healing. S. divinorum has over the last several years gained increased popularity as a recreational drug. This is a double-blind, placebo controlled study of salvinorin A in 4 psychologically and physically healthy hallucinogen-using adults. Across sessions, participants inhaled 16 ascending doses of salvinorin A and 4 intermixed placebo doses under comfortable and supportive conditions. Doses ranged from 0.375 μg/kg to 21 μg/kg. Subject-rated drug strength was assessed every 2 min for 60 min after inhalation. Orderly time- and dose-related effects were observed. Drug strength ratings peaked at 2 min (first time point) and definite subjective effects were no longer present at approximately 20 min after inhalation. Dose-related increases were observed on questionnaire measures of mystical-type experience (Mysticism Scale) and subjective effects associated with classic serotonergic (5-HT2(A)) hallucinogens (Hallucinogen Rating Scale). Salvinorin A did not significantly increase heart rate or blood pressure. Participant narratives indicated intense experiences characterized by disruptions in vestibular and interoceptive signals (e.g., change in spatial orientation, pressure on the body) and unusual and sometimes recurring themes across sessions such as revisiting childhood memories, cartoon-like imagery, and contact with entities. Under these prepared and supportive conditions, salvinorin A occasioned a unique profile of subjective effects having similarities to classic hallucinogens, including mystical-type effects.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Baggott MJ, Erowid E, Erowid F, Galloway GP, Mendelson J. Use patterns and self-reported effects of Salvia divinorum: An internet-based survey. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010;111:250–6. - PubMed
-
- Braida D, Limonta V, Capurro V, Fadda P, Rubino T, Mascia P, Zani A, Gori E, Fratta W, Parolaro D, Sala M. Involvement of kappa-opioid and endocannabinoid system on Salvinorin A-induced reward. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:286–92. - PubMed
-
- Bücheler R, Gleiter CH, Schwoerer P, Gaertner I. Use of nonprohibited hallucinogenic plants: increasing relevance for public health? A case report and literature review on the consumption of Salvia divinorum (Diviner’s Sage) Pharmacopsychiatry. 2005;38:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Butelman ER, Harris TJ, Kreek MJ. The plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, produces kappa-opioid agonist-like discriminative effects in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology. 2004;172:220–224. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr, Beguin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Lee DY, Cohen BM. Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;316:440–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

