Divergent GW182 functional domains in the regulation of translational silencing
- PMID: 21131274
- PMCID: PMC3074120
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1099
Divergent GW182 functional domains in the regulation of translational silencing
Abstract
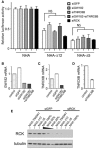
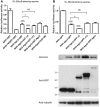
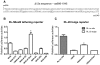
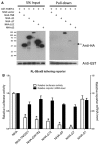
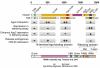
MicroRNA (miRNA)-mediated gene regulation has become a major focus in many biological processes. GW182 and its long isoform TNGW1 are marker proteins of GW/P bodies and bind to Argonaute proteins of the RNA induced silencing complex. The goal of this study is to further define and distinguish the repression domain(s) in human GW182/TNGW1. Two non-overlapping regions, Δ12 (amino acids 896-1219) containing the Ago hook and Δ5 (amino acids 1670-1962) containing the RRM, both induced comparable silencing in a tethering assay. Mapping data showed that the RRM and its flanking sequences in Δ5, but not the Ago hook in Δ12, were important for silencing. Repression mediated by Δ5 or Δ12 was not differentially affected when known endogenous repressors RCK/p54, GW182/TNGW1, TNRC6B were depleted. Transfected Δ5, but not Δ12, enhanced Ago2-mediated repression in a tethering assay. Transfected Δ12, but not Δ5, released endogenous miRNA reporter silencing without affecting siRNA function. Alanine substitution showed that GW/WG motifs in Δ12 (Δ12a, amino acids 896-1045) were important for silencing activity. Although Δ12 appeared to bind PABPC1 more efficiently than Δ5, neither Δ5 nor Δ12 significantly enhanced reporter mRNA degradation. These different functional characteristics of Δ5 and Δ12 suggest that their roles are distinct, and possibly dynamic, in human GW182-mediated silencing.
Figures
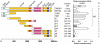

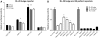
Similar articles
-
Function of GW182 and GW bodies in siRNA and miRNA pathways.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:71-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224966 Review.
-
Identification of GW182 and its novel isoform TNGW1 as translational repressors in Ago2-mediated silencing.J Cell Sci. 2008 Dec 15;121(Pt 24):4134-44. doi: 10.1242/jcs.036905. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 19056672 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian GW182 contains multiple Argonaute-binding sites and functions in microRNA-mediated translational repression.RNA. 2009 Jun;15(6):1078-89. doi: 10.1261/rna.1363109. Epub 2009 Apr 27. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19398495 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal half of human Ago2 binds to multiple GW-rich regions of GW182 and requires GW182 to mediate silencing.RNA. 2009 May;15(5):804-13. doi: 10.1261/rna.1229409. Epub 2009 Mar 26. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19324964 Free PMC article.
-
The role of GW182 proteins in miRNA-mediated gene silencing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:147-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224969 Review.
Cited by
-
KSHV RNA-binding protein ORF57 inhibits P-body formation to promote viral multiplication by interaction with Ago2 and GW182.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 26;47(17):9368-9385. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz683. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31400113 Free PMC article.
-
Phase Transitions in the Assembly and Function of Human miRISC.Cell. 2018 May 3;173(4):946-957.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.051. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29576456 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis.FEBS Lett. 2011 Dec 1;585(23):3667-74. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.05.020. Epub 2011 May 14. FEBS Lett. 2011. PMID: 21600203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capturing microRNA targets using an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)-trap approach.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Dec 11;109(50):20473-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218887109. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23184980 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of pathological pathways centered on circRNA dysregulation in association with irreversible progression of Alzheimer's disease.Genome Med. 2024 Nov 11;16(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13073-024-01404-6. Genome Med. 2024. PMID: 39529134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010;79:351–379. - PubMed
-
- Chekulaeva M, Filipowicz W. Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009;21:452–460. - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell. 2008;132:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

