Regulatory modules function in a non-autonomous manner to control transcription of the mbp gene
- PMID: 21131280
- PMCID: PMC3074125
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1160
Regulatory modules function in a non-autonomous manner to control transcription of the mbp gene
Abstract
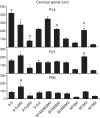
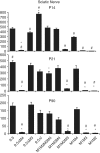
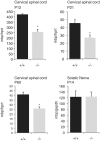
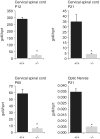
Multiple regulatory modules contribute to the complex expression programs realized by many loci. Although long thought of as isolated components, recent studies demonstrate that such regulatory sequences can physically associate with promoters and with each other and may localize to specific sub-nuclear transcription factories. These associations provide a substrate for putative interactions and have led to the suggested existence of a transcriptional interactome. Here, using a controlled strategy of transgenesis, we analyzed the functional consequences of regulatory sequence interaction within the myelin basic protein (mbp) locus. Interactions were revealed through comparisons of the qualitative and quantitative expression programs conferred by an allelic series of 11 different enhancer/inter-enhancer combinations ligated to a common promoter/reporter gene. In a developmentally contextual manner, the regulatory output of all modules changed markedly in the presence of other sequences. Predicted by transgene expression programs, deletion of one such module from the endogenous locus reduced oligodendrocyte expression levels but unexpectedly, also attenuated expression of the overlapping golli transcriptional unit. These observations support a regulatory architecture that extends beyond a combinatorial model to include frequent interactions capable of significantly modulating the functions conferred through regulatory modules in isolation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulators of the Golli/myelin basic protein locus integrate additive and stealth activities.PLoS Genet. 2020 Aug 13;16(8):e1008752. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008752. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32790717 Free PMC article.
-
A combinatorial network of evolutionarily conserved myelin basic protein regulatory sequences confers distinct glial-specific phenotypes.J Neurosci. 2003 Nov 12;23(32):10214-23. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-32-10214.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14614079 Free PMC article.
-
A distal upstream enhancer from the myelin basic protein gene regulates expression in myelin-forming schwann cells.J Neurosci. 2001 Jun 1;21(11):3780-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-11-03780.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11356866 Free PMC article.
-
Myelin basic protein gene contains separate enhancers for oligodendrocyte and Schwann cell expression.J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):605-16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.605. J Cell Biol. 1992. PMID: 1383235 Free PMC article.
-
The pathobiology of myelin mutants reveal novel biological functions of the MBP and PLP genes.Brain Pathol. 2001 Jan;11(1):74-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2001.tb00383.x. Brain Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11145205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oligodendrocyte HCN2 Channels Regulate Myelin Sheath Length.J Neurosci. 2021 Sep 22;41(38):7954-7964. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2463-20.2021. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34341156 Free PMC article.
-
Myelin basic protein mRNA levels affect myelin sheath dimensions, architecture, plasticity, and density of resident glial cells.Glia. 2024 Oct;72(10):1893-1914. doi: 10.1002/glia.24589. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Glia. 2024. PMID: 39023138 Free PMC article.
-
A dual role for DNA binding by Runt in activation and repression of sloppy paired transcription.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Nov 1;32(21):ar26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-08-0509. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34432496 Free PMC article.
-
Ever-Changing Landscapes: Transcriptional Enhancers in Development and Evolution.Cell. 2016 Nov 17;167(5):1170-1187. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.018. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27863239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted insertion of two Mthfr promoters in mice reveals temporal- and tissue-specific regulation.Mamm Genome. 2011 Dec;22(11-12):635-47. doi: 10.1007/s00335-011-9351-5. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Mamm Genome. 2011. PMID: 21769670
References
-
- Loots GG, Locksley RM, Blankespoor CM, Wang ZE, Miller W, Rubin EM, Frazer KA. Identification of a coordinate regulator of interleukins 4, 13, and 5 by cross-species sequence comparisons. Science. 2000;288:136–140. - PubMed
-
- Pennacchio LA, Rubin EM. Genomic strategies to identify mammalian regulatory sequences. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001;2:100–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

