A simple method using PyrosequencingTM to identify de novo SNPs in pooled DNA samples
- PMID: 21131285
- PMCID: PMC3061071
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1249
A simple method using PyrosequencingTM to identify de novo SNPs in pooled DNA samples
Abstract
A practical way to reduce the cost of surveying single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in a large number of individuals is to measure the allele frequencies in pooled DNA samples. Pyrosequencing(TM) has been frequently used for this application because signals generated by this approach are proportional to the amount of DNA templates. The Pyrosequencing(TM) pyrogram is determined by the dispensing order of dNTPs, which is usually designed based on the known SNPs to avoid asynchronistic extensions of heterozygous sequences. Therefore, utilizing the pyrogram signals to identify de novo SNPs in DNA pools has never been undertook. Here, in this study we developed an algorithm to address this issue. With the sequence and pyrogram of the wild-type allele known in advance, we could use the pyrogram obtained from the pooled DNA sample to predict the sequence of the unknown mutant allele (de novo SNP) and estimate its allele frequency. Both computational simulation and experimental Pyrosequencing(TM) test results suggested that our method performs well. The web interface of our method is available at http://life.nctu.edu.tw/∼yslin/PSM/.
Figures
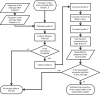
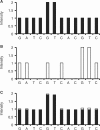
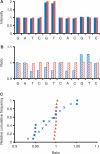
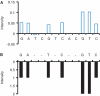
Similar articles
-
Efficient identification of SNPs in pooled DNA samples using a dual mononucleotide addition-based sequencing method.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Oct;292(5):1069-1081. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1332-2. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28612167 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrosequencing-based SNP allele frequency estimation in DNA pools.Hum Mutat. 2004 Jan;23(1):92-7. doi: 10.1002/humu.10292. Hum Mutat. 2004. PMID: 14695537
-
Estimation of single nucleotide polymorphism allele frequency in DNA pools by using Pyrosequencing.Hum Genet. 2002 May;110(5):395-401. doi: 10.1007/s00439-002-0722-6. Epub 2002 Apr 9. Hum Genet. 2002. PMID: 12073008
-
Fundamentals of pyrosequencing.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013 Sep;137(9):1296-303. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0463-RA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23991743 Review.
-
Pyrosequencing: nucleotide sequencing technology with bacterial genotyping applications.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2005 Nov;5(6):947-53. doi: 10.1586/14737159.5.6.947. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2005. PMID: 16255635 Review.
Cited by
-
Rhizodegradation of PAHs differentially altered by C3 and C4 plants.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 30;10(1):16109. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72844-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32999304 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient identification of SNPs in pooled DNA samples using a dual mononucleotide addition-based sequencing method.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Oct;292(5):1069-1081. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1332-2. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28612167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sham P, Bader JS, Craig I, O'Donovan M, Owen M. DNA Pooling: a tool for large-scale association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002;3:862–871. - PubMed
-
- Risch N, Teng J. The relative power of family-based and case-control designs for linkage disequilibrium studies of complex human diseases I. DNA pooling. Genome Res. 1998;8:1273–1288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

