Downregulation of NCC and NKCC2 cotransporters by kidney-specific WNK1 revealed by gene disruption and transgenic mouse models
- PMID: 21131289
- PMCID: PMC3033178
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq525
Downregulation of NCC and NKCC2 cotransporters by kidney-specific WNK1 revealed by gene disruption and transgenic mouse models
Abstract
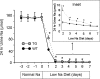
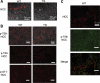
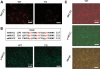
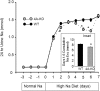
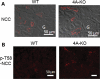
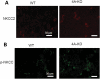
WNK1 (with-no-lysine[K]-1) is a protein kinase of which mutations cause a familial hypertension and hyperkalemia syndrome known as pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2 (PHA2). Kidney-specific (KS) WNK1 is an alternatively spliced form of WNK1 kinase missing most of the kinase domain. KS-WNK1 downregulates the Na(+)-Cl(-) cotransporter NCC by antagonizing the effect of full-length WNK1 when expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The physiological role of KS-WNK1 in the regulation of NCC and potentially other Na(+) transporters in vivo is unknown. Here, we report that mice overexpressing KS-WNK1 in the kidney exhibited renal Na(+) wasting, elevated plasma levels of angiotensin II and aldosterone yet lower blood pressure relative to wild-type littermates. Immunofluorescent staining revealed reduced surface expression of total and phosphorylated NCC and the Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl(-) cotransporter NKCC2 in the distal convoluted tubule and the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop, respectively. Conversely, mice with targeted deletion of exon 4A (the first exon for KS-WNK1) exhibited Na(+) retention, elevated blood pressure on a high-Na(+) diet and increased surface expression of total and phosphorylated NCC and NKCC2 in respective nephron segments. Thus, KS-WNK1 is a negative regulator of NCC and NKCC2 in vivo and plays an important role in the control of Na(+) homeostasis and blood pressure. These results have important implications to the pathogenesis of PHA2 with WNK1 mutations.
Figures
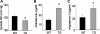


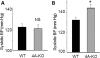
References
-
- Xu B., English J.M., Wilsbacher J.L., Stippec S., Goldsmith E.J., Cobb M.H. WNK1, a novel mammalian serine/threonine protein kinase lacking the catalytic lysine in subdomain II. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:16795–16801. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.22.16795. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilson F.H., Disse-Nicodème S., Choate K.A., Ishikawa K., Nelson-Williams C., Desitter I., Gunel M., Milford D.V., Lipkin G.W., Achard J.M., et al. Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science. 2001;293:1107–1112. doi:10.1126/science.1062844. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Veríssimo F., Jordan P. WNK kinases, a novel protein kinase subfamily in multi-cellular organisms. Oncogene. 2001;20:5562–5569. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204726. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilson F.H., Kahle K.T., Sabath E., Lalioti M.D., Rapson A.K., Hoover R.S., Hebert S.C., Gamba G., Lifton R.P. Molecular pathogenesis of inherited hypertension with hyperkalemia: the Na-Cl cotransporter is inhibited by wild-type but not mutant WNK4. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:680–684. doi:10.1073/pnas.242735399. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

