Induction of miR-21 by retinoic acid in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinoma cells: biological correlates and molecular targets
- PMID: 21131358
- PMCID: PMC3030403
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.184994
Induction of miR-21 by retinoic acid in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinoma cells: biological correlates and molecular targets
Abstract
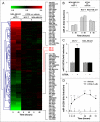
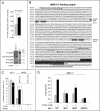
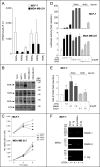
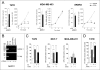
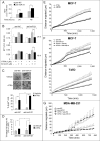
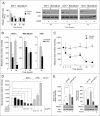
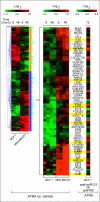
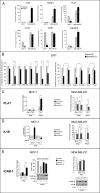
Retinoids are promising agents for the treatment/prevention of breast carcinoma. We examined the role of microRNAs in mediating the effects of all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA), which suppresses the proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive (ERα(+)) breast carcinoma cells, such as MCF-7, but not estrogen receptor-negative cells, such as MDA-MB-231. We found that pro-oncogenic miR-21 is selectively induced by ATRA in ERα(+) cells. Induction of miR-21 counteracts the anti-proliferative action of ATRA but has the potentially beneficial effect of reducing cell motility. In ERα(+) cells, retinoid-dependent induction of miR-21 is due to increased transcription of the MIR21 gene via ligand-dependent activation of the nuclear retinoid receptor, RARα. RARα is part of the transcription complex present in the 5'-flanking region of the MIR21 gene. The receptor binds to two functional retinoic acid-responsive elements mapping upstream of the transcription initiation site. Silencing of miR-21 enhances ATRA-dependent growth inhibition and senescence while reverting suppression of cell motility afforded by the retinoid. Up-regulation of miR-21 results in retinoid-dependent inhibition of the established target, maspin. Knockdown and overexpression of maspin in MCF-7 cells indicates that the protein is involved in ATRA-induced growth inhibition and contributes to the ATRA-dependent anti-motility responses. Integration between whole genome analysis of genes differentially regulated by ATRA in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells, prediction of miR-21 regulated genes, and functional studies led to the identification of three novel direct miR-21 targets: the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL1B, the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 and PLAT, the tissue-type plasminogen activator. Evidence for ICAM-1 involvement in retinoid-dependent inhibition of MCF-7 cell motility is provided.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of all-trans retinoic acid-induced MiRNA expression in neoplastic cell lines: a systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 30;19(1):866. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6081-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31470825 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans-retinoic acid modulates glycolysis via H19 and telomerase: the role of mir-let-7a in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2024 May 21;24(1):615. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12379-3. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38773429 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular determinants of all-trans retinoic acid sensitivity in breast cancer: Luminal phenotype and RARα expression.EMBO Mol Med. 2015 Jul;7(7):950-72. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201404670. EMBO Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25888236 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of estrogen receptor alpha, retinoic acid receptor alpha and cellular retinoic acid binding protein II genes is coordinately regulated in human breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2005 Jun 23;24(27):4362-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208661. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 15870697
-
Complexity, retinoid-responsive gene networks, and bladder carcinogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;462:449-67. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4737-2_35. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10599447 Review.
Cited by
-
Leukemia cell-derived microvesicles induce T cell exhaustion via miRNA delivery.Oncoimmunology. 2018 Mar 26;7(7):e1448330. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1448330. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2018. PMID: 29900066 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in cancer therapeutic response: Friend and foe.World J Clin Oncol. 2014 Oct 10;5(4):730-43. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.730. World J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25302173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The miRNA: a small but powerful RNA for COVID-19.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Mar 22;22(2):1137-1149. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab062. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33675361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of all-trans retinoic acid-induced MiRNA expression in neoplastic cell lines: a systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2019 Aug 30;19(1):866. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6081-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31470825 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics identification of dysregulated microRNAs in triple negative breast cancer based on microRNA expression profiling.Oncol Lett. 2018 Mar;15(3):3017-3023. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7707. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29435032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garattini E., Gianni M., Terao M. (2007) Curr. Pharm. Des. 13, 1375–1400 - PubMed
-
- Garattini E., Gianni M., Terao M. (2004) Curr. Pharm. Des. 10, 433–448 - PubMed
-
- Uray I. P., Brown P. H. (2006) Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 15, 1583–1600 - PubMed
-
- Brodersen P., Voinnet O. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 141–148 - PubMed
-
- Gregory P. A., Bert A. G., Paterson E. L., Barry S. C., Tsykin A., Farshid G., Vadas M. A., Khew-Goodall Y., Goodall G. J. (2008) Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 593–601 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

