The fungal type II myosin in Penicillium marneffei, MyoB, is essential for chitin deposition at nascent septation sites but not actin localization
- PMID: 21131434
- PMCID: PMC3067470
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00201-10
The fungal type II myosin in Penicillium marneffei, MyoB, is essential for chitin deposition at nascent septation sites but not actin localization
Abstract
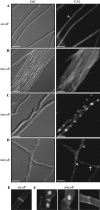
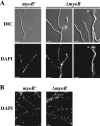
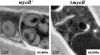
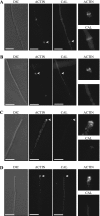
Cytokinesis is essential for proliferative growth but also plays equally important roles during morphogenesis and development. The human pathogen Penicillium marneffei is capable of dimorphic switching in response to temperature, growing in a multicellular filamentous hyphal form at 25°C and in a unicellular yeast form at 37°C. P. marneffei also undergoes asexual development at 25°C to produce multicellular differentiated conidiophores. Thus, P. marneffei exhibits cell division with and without cytokinesis and division by budding and fission, depending on the cell type. The type II myosin gene, myoB, from P. marneffei plays important roles in the morphogenesis of these cell types. Deletion of myoB leads to chitin deposition defects at sites of cell division without perturbing actin localization. In addition to aberrant hyphal cells, distinct conidiophore cell types are lacking due to malformed septa and nuclear division defects. At 37°C, deletion of myoB prevents uninucleate yeast cell formation, instead producing long filaments resembling hyphae at 25°C. The ΔmyoB cells also often lyse due to defects in cell wall biogenesis. Thus, MyoB is essential for correct morphogenesis of all cell types regardless of division mode (budding or fission) and defines differences between the different types of growth.
Figures




References
-
- Almonacid M., et al. 2009. Spatial control of cytokinesis by Cdr2 kinase and Mid1/anillin nuclear export. Curr. Biol. 19:961–966 - PubMed
-
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403–410 - PubMed
-
- Andrianopoulos A. 2002. Control of morphogenesis in the human fungal pathogen Penicillium marneffei. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 292:331–347 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

