Segmental allergen challenge alters multimeric structure and function of surfactant protein D in humans
- PMID: 21131470
- PMCID: PMC3086753
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201004-0654OC
Segmental allergen challenge alters multimeric structure and function of surfactant protein D in humans
Abstract
Rationale: Surfactant protein D (SP-D), a 43-kD collectin, is synthesized and secreted by airway epithelia as a dodecamer formed by assembly of four trimeric subunits. We have previously shown that the quaternary structure of SP-D can be altered during inflammatory lung injury through its modification by S-nitrosylation, which in turn alters its functional behavior producing a proinflammatory response in effector cells.
Objectives: We hypothesized that alterations in structure and function of SP-D may occur in humans with acute allergic inflammation.
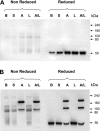
Methods: Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid was collected from 15 nonsmoking patients with mild intermittent allergic asthma before and 24 hours after segmental provocation with saline, allergen, LPS, and mixtures of allergen and LPS. Structural modifications of SP-D were analyzed by native and sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis.
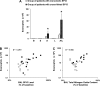
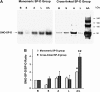
Measurements and main results: The multimeric structure of native SP-D was found to be disrupted after provocation with allergen or a mixture of allergen and LPS. Interestingly, under reducing conditions, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis demonstrated that 7 of 15 patients with asthma developed an abnormal cross-linked SP-D band after segmental challenge with either allergen or a mixture of allergen with LPS but not LPS alone. Importantly, patients with asthma with cross-linked SP-D demonstrated significantly higher levels of BAL eosinophils, nitrogen oxides, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and S-nitrosothiol-SP-D compared with patients without cross-linked SP-D.
Conclusions: We conclude that segmental allergen challenge results in changes of SP-D multimeric structure and that these modifications are associated with an altered local inflammatory response in the distal airways.
Figures

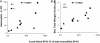

References
-
- Drickamer K. Ca2+-dependent carbohydrate-recognition domains in animal proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 1993;3:393–400.
-
- Voorhout WF, Veenendaal T, Kuroki Y, Ogasawara Y, Vangolde LMG, Geuze HJ. Immunocytochemical localization of surfactant protein-d (SP-D) in type-II cells, Clara cells, and alveolar macrophages of rat lung. J Histochem Cytochem 1992;40:1589–1597. - PubMed
-
- Wong CJ, Akiyama J, Allen L, Hawgood S. Localization and developmental expression of surfactant proteins D and A in the respiratory tract of the mouse. Pediatr Res 1996;39:930–937. - PubMed
-
- Wright JR. Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol 2005;5:58–68. - PubMed
-
- Crouch E, Persson A, Chang D, Heuser J. Molecular-structure of pulmonary surfactant protein-D (SP-D). J Biol Chem 1994;269:17311–17319. - PubMed

