Constitutive expression of the maltoporin LamB in the absence of OmpR damages the cell envelope
- PMID: 21131484
- PMCID: PMC3028690
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01004-10
Constitutive expression of the maltoporin LamB in the absence of OmpR damages the cell envelope
Abstract
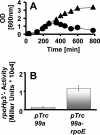
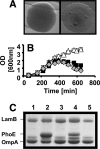
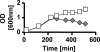
Cells experience multiple environmental stimuli simultaneously. To survive, they must respond accordingly. Unfortunately, the proper response to one stress easily could make the cell more susceptible to a second coexistent stress. To deal with such a problem, a cell must possess a mechanism that balances the need to respond simultaneously to both stresses. Our recent studies of ompR malT(Con) double mutants show that elevated expression of LamB, the outer membrane porin responsible for maltose uptake, causes cell death when the osmoregulator OmpR is disabled. To obtain insight into the nature of the death experienced by ompR malT(Con) mutants, we described the death process. On the basis of microscopic and biochemical approaches, we conclude that death results from a loss of membrane integrity. On the basis of an unbiased genome-wide search for suppressor mutations, we conclude that this loss of membrane integrity results from a LamB-induced envelope stress that the cells do not sufficiently perceive and thus do not adequately accommodate. Finally, we conclude that this envelope stress involves an imbalance in the lipopolysaccharide/porin composition of the outer membrane and an increased requirement for inorganic phosphate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of pleiotropic ompR and envZ alleles of Escherichia coli on envelope stress and antibiotic sensitivity.J Bacteriol. 2024 Jun 20;206(6):e0017224. doi: 10.1128/jb.00172-24. Epub 2024 May 29. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38809006 Free PMC article.
-
A critical process controlled by MalT and OmpR is revealed through synthetic lethality.J Bacteriol. 2009 Aug;191(16):5320-4. doi: 10.1128/JB.00522-09. Epub 2009 Jun 5. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19502392 Free PMC article.
-
Signal sequence processing is required for the assembly of LamB trimers in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3327-34. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3327-3334.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8501036 Free PMC article.
-
[Escherichia coli phage receptors. Minor porins and proteins participating in the specific transport as phage receptors].Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1989 Dec;(12):3-12. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1989. PMID: 2561376 Review. Russian.
-
Interaction of bacteriophage l with its E. coli receptor, LamB.Viruses. 2012 Nov 15;4(11):3162-78. doi: 10.3390/v4113162. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23202520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The ColRS system is essential for the hunger response of glucose-growing Pseudomonas putida.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Jul 26;11:170. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-170. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21791104 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling of Vibrio cholerae O1 following exposure to human anti- lipopolysaccharide monoclonal antibodies.Pathog Dis. 2020 Jun 1;78(4):ftaa029. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftaa029. Pathog Dis. 2020. PMID: 32589220 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to Glycolytic Carbon Sources Reveals a Novel Layer of Regulation for the MalT Regulon.Int J Microbiol. 2011;2011:107023. doi: 10.1155/2011/107023. Epub 2011 Aug 14. Int J Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21912549 Free PMC article.
-
Phage shock proteins B and C prevent lethal cytoplasmic membrane permeability in Yersinia enterocolitica.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Aug;85(3):445-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08120.x. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22646656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alba, B. M., and C. A. Gross. 2004. Regulation of the Escherichia coli sigma-dependent envelope stress response. Mol. Microbiol. 52:613-619. - PubMed
-
- Amemura, M., K. Makino, H. Shinagawa, A. Kobayashi, and A. Nakata. 1985. Nucleotide sequence of the genes involved in phosphate transport and regulation of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 184:241-250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

