Characterization of a novel beta-xylosidase, XylC, from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum JW/SL-YS485
- PMID: 21131522
- PMCID: PMC3028745
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01511-10
Characterization of a novel beta-xylosidase, XylC, from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum JW/SL-YS485
Abstract
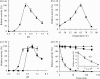
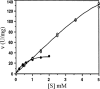
The 1,914-bp open reading frame of xylC from Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum JW/SL-YS485 encodes a calculated 73-kDa β-xylosidase, XylC, different from any glycosyl hydrolase in the database and representing a novel glycohydrolase family. Hydrolysis occurred under retention of the anomeric configuration, and transglycosylation occurred in the presence of alcohols as acceptors. With the use of vector pHsh, expression of XylC, the third β-xylosidase in this bacterium, increased approximately 4-fold when a loop within the translational initiation region in the mRNA was removed by site-directed mutagenesis. The increased expression of xylC(m) is due to removal of a stem-loop structure without a change of the amino acid sequence of the heterologously expressed enzyme (XylC(rec)). When gel filtration was applied, purified XylC had molecular masses of 210 kDa and 265 kDa using native gradient gel electrophoresis. The protein consisted of 78-kDa subunits based on SDS gel electrophoresis and contained 6% carbohydrates. XylC and XylC(rec) exhibited maximum activity at 65°C and pH(65°C) 6.0, a 1-h half-life at 67°C, a K(m) for p-nitrophenyl-β-D-xyloside of 28 mM, and a V(max) of 276 U/mg and retained 70% activity in the presence of 200 mM xylose, suggesting potential for industrial applications.
Figures




References
-
- Biely, P. 1985. Microbial xylanolytic systems. Trends Biotechnol. 3:286-290.
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Brux, C., et al. 2006. The structure of an inverting GH43 beta-xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus with its substrate reveals the role of the three catalytic residues. J. Mol. Biol. 359:97-109. - PubMed
-
- Cournoyer, B., and D. Faure. 2003. Radiation and functional specialization of the family-3 glycoside hydrolases. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 5:190-198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

