The yctCBA operon of Yersinia ruckeri, involved in in vivo citrate uptake, is not required for virulence
- PMID: 21131526
- PMCID: PMC3028698
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01808-10
The yctCBA operon of Yersinia ruckeri, involved in in vivo citrate uptake, is not required for virulence
Abstract
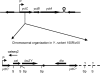
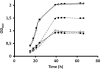
A three-gene operon, named yctCBA (Yersinia citrate transporter), induced by citrate and repressed by glucose was identified from a previously selected in vivo-induced (ivi) clone in the fish pathogen Yersinia ruckeri. Interestingly, despite being an ivi clone, the drastic growth reduction of the yctC mutant in the presence of citrate, and the relatively high content of this compound in rainbow trout serum, the operon was not required for virulence.
Figures
References
-
- Antoine, R., et al. 2005. The periplasmic binding protein of a tripartite tricarboxylate transporter is involved in signal transduction. J. Mol. Biol. 351:799-809. - PubMed
-
- Arias, C. R., et al. 2007. First report of Yersinia ruckeri biotype 2 in the USA. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 19:35-40. - PubMed
-
- Austin, D. A., P. A. W. Robertson, and B. Austin. 2003. Recovery of a new biogroup of Yersinia ruckeri from diseased rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 26:127-131. - PubMed
-
- Austin, B., and D. A. Austin. 2007. Bacterial fish pathogens: diseases of farmed and wild fish, 4th ed. Springer-Praxis, Godalming, United Kingdom.
-
- Bott, M. 1997. Anaerobic citrate metabolism and its regulation in enterobacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 167:78-88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

