Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by TCDD reduces inflammation associated with Crohn's disease
- PMID: 21131560
- PMCID: PMC3044199
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq360
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by TCDD reduces inflammation associated with Crohn's disease
Abstract
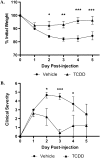
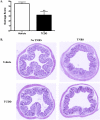
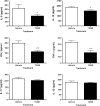
Crohn's disease results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors that trigger an inappropriate immune response to commensal gut bacteria. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is well known for its involvement in the toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), an environmental contaminant that affects people primarily through the diet. Recently, TCDD was shown to suppress immune responses by generating regulatory T cells (Tregs). We hypothesized that AhR activation dampens inflammation associated with Crohn's disease. To test this hypothesis, we utilized the 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS) murine model of colitis. Mice were gavaged with TCDD prior to colitis induction with TNBS. Several parameters were examined including colonic inflammation via histological and flow cytometric analyses. TCDD-treated mice recovered body weight faster and experienced significantly less colonic damage. Reduced levels of interleukin (IL) 6, IL-12, interferon-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor-α demonstrated suppression of inflammation in the gut following TCDD exposure. Forkhead box P3 (Foxp3)(egfp) mice revealed that TCDD increased the Foxp3+ Treg population in gut immune tissue following TNBS exposure. Collectively, these results suggest that activation of the AhR by TCDD decreases colonic inflammation in a murine model of colitis in part by generating regulatory immune cells. Ultimately, this work may lead to the development of more effective therapeutics for the treatment of Crohn's disease.
Figures
References
-
- Abraham C, Cho JH. IL-23 and autoimmunity: new insights into the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009;60:97–110. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S. Molecular targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006;71:1397–1421. - PubMed
-
- Baumgart DC, Dignass AU. Intestinal barrier function. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2002;5:685–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

