Palmitoylation regulates raft affinity for the majority of integral raft proteins
- PMID: 21131568
- PMCID: PMC3009825
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1016184107
Palmitoylation regulates raft affinity for the majority of integral raft proteins
Abstract
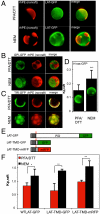
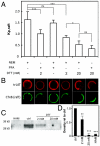
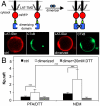
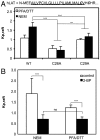
The physical basis for protein partitioning into lipid rafts remains an outstanding question in membrane biology that has previously been addressed only through indirect techniques involving differential solubilization by nonionic detergents. We have used giant plasma membrane vesicles, a plasma membrane model system that phase separates to include an ordered phase enriching for raft constituents, to measure the partitioning of the transmembrane linker for activation of T cells (LAT). LAT enrichment in the raft phase was dependent on palmitoylation at two juxtamembrane cysteines and could be enhanced by oligomerization. This palmitoylation requirement was also shown to regulate raft phase association for the majority of integral raft proteins. Because cysteine palmitoylation is the only lipid modification that has been shown to be reversibly regulated, our data suggest a role for palmitoylation as a dynamic raft targeting mechanism for transmembrane proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Resh MD. Palmitoylation of ligands, receptors, and intracellular signaling molecules. Sci STKE. 2006;2006:re14. - PubMed
-
- Melkonian KA, Ostermeyer AG, Chen JZ, Roth MG, Brown DA. Role of lipid modifications in targeting proteins to detergent-resistant membrane rafts. Many raft proteins are acylated, while few are prenylated. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:3910–3917. - PubMed
-
- Moffett S, Brown DA, Linder ME. Lipid-dependent targeting of G proteins into rafts. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2191–2198. - PubMed
-
- Rocks O, et al. An acylation cycle regulates localization and activity of palmitoylated Ras isoforms. Science. 2005;307:1746–1752. - PubMed
-
- Webb Y, Hermida-Matsumoto L, Resh MD. Inhibition of protein palmitoylation, raft localization, and T cell signaling by 2-bromopalmitate and polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:261–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

