MR CONTRAST SYNTHESIS FOR LESION SEGMENTATION
- PMID: 21132059
- PMCID: PMC2995277
- DOI: 10.1109/ISBI.2010.5490140
MR CONTRAST SYNTHESIS FOR LESION SEGMENTATION
Abstract
The magnetic resonance contrast of a neuroimaging data set has strong impact on the utility of the data in image analysis tasks, such as registration and segmentation. Lengthy acquisition times often prevent routine acquisition of multiple MR contrast images, and opportunities for detailed analysis using these data would seem to be irrevocably lost. This paper describes an example based approach which uses patch matching from a multiple contrast atlas with the intended goal of generating an alternate MR contrast image, thus effectively simulating alternative pulse sequences from one another. In this paper, we deal specifically with Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) sequence generation from T1 and T2 pulse sequences. The applicability of this synthetic FLAIR for estimating white matter lesions segmentation is demonstrated.
Figures
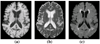
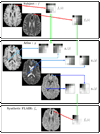
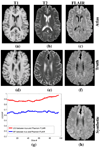
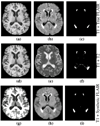
Similar articles
-
Synthesizing MR Contrast and Resolution through a Patch Matching Technique.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2010;7623:76230j. doi: 10.1117/12.844575. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2010. PMID: 20431709 Free PMC article.
-
T1-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery and T1-weighted fast spin-echo contrast-enhanced imaging: a comparison in 20 patients with brain lesions.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2009 Aug;53(4):366-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1754-9485.2009.02093.x. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19695043
-
Relationship between contrast enhancement on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR sequences and signal intensity on T2-weighted MR images: visual evaluation of brain tumors.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005 Jun;21(6):694-700. doi: 10.1002/jmri.20331. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005. PMID: 15906343
-
New options for increasing the sensitivity, specificity and scope of synergistic contrast magnetic resonance imaging (scMRI) using Multiplied, Added, Subtracted and/or FiTted (MASTIR) pulse sequences.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020 Oct;10(10):2030-2065. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-795. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 33014733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR): clinical prospectus of current and future applications.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 1996 Dec;8(6):389-96. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 1996. PMID: 9402679 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-local statistical label fusion for multi-atlas segmentation.Med Image Anal. 2013 Feb;17(2):194-208. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Med Image Anal. 2013. PMID: 23265798 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating CT Image From MRI Data Using Structured Random Forest and Auto-Context Model.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016 Jan;35(1):174-83. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2461533. Epub 2015 Jul 28. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26241970 Free PMC article.
-
Example Based Lesion Segmentation.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2014 Feb 15;9034:90341Y. doi: 10.1117/12.2043917. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2014. PMID: 27795605 Free PMC article.
-
Is synthesizing MRI contrast useful for inter-modality analysis?Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2013;16(Pt 1):631-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-40811-3_79. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2013. PMID: 24505720 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-core steered non-rigid registration for multi-modal images via bi-directional image synthesis.Med Image Anal. 2017 Oct;41:18-31. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 13. Med Image Anal. 2017. PMID: 28533050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI. Cortical Surface-Based Analysis i: Segmentation and Surface Reconstruction. NeuroImage. 1999;vol. 9(no. 2):179–194. - PubMed
-
- Bazin PL, Pham DL. Topology-Preserving Tissue Classification of Magnetic Resonance Brain Images. IEEE Trans. on Med. Imag. 2007;vol. 26(no. 4):487–498. - PubMed
-
- Hong X, McClean S, Scotney B, Morrow P. Model-Based Segmentation of Multimodal Images. Comp. Anal. of Images and Patterns. 2007;vol. 4672:604–611.
-
- Fischl B, Salat DH, van der Kouwe AJW, Makris N, Segonne F, Quinn BT, Dale AM. Sequence-independent Segmentation of Magnetic Resonance Images. NeuroImage. 2004;vol. 23:S69–S84. - PubMed
-
- Filippi M, Yousry T, Baratti C, Horsfield MA, Mammi S, Becker C, Voltz R, Spuler S, Campi A, Reiser MF, Comi G. Quantitative Assessment of MRI Lesion Load in Multiple Sclerosis, A comparison of conventional spin-echo with fast fluidattenuated inversion recovery. Brain. 1996;vol. 119:1349–1355. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
