Actively targeted low-dose camptothecin as a safe, long-acting, disease-modifying nanomedicine for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 21132352
- PMCID: PMC3789645
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-010-0330-4
Actively targeted low-dose camptothecin as a safe, long-acting, disease-modifying nanomedicine for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Purpose: Camptothecin (CPT), a potent topoisomerase I inhibitor, was originally discovered as an anticancer agent to induce programmed cell death of cancer cells. Recent evidence suggests that, similar to cancer, alterations in apoptosis and over-proliferation of key effector cells in the arthritic joint result in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathogenesis. Initial in vitro studies have suggested that camptothecin inhibits synoviocyte proliferation, matrix metalloproteinases expression in chrondrocytes and angiogenesis. This study is one of the first to test, in vivo, RA as a new indication for CPT.
Methods: To circumvent insolubility, instability and toxicity of CPT, we used biocompatible, biodegradable and targeted sterically stabilized micelles (SSM) as nanocarriers for CPT (CPT-SSM). We also surface-modified CPT-SSM with vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) for active targeting. We then determined whether this nanomedicine abrogated collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice.
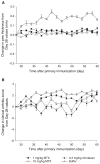
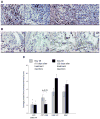
Results: Based on our findings, this is the first study to report that CPT was found to be efficacious against CIA at concentrations significantly lower than usual anti-cancer dose. Furthermore, a single subcutaneous injection of CPT-SSM-VIP (0.1 mg/kg) administered to CIA mice mitigated joint inflammation for at least 32 days thereafter without systemic toxicity. CPT alone needed at least 10-fold higher dose to achieve the same effect, albeit with some vacuolization in liver histology.
Conclusion: We propose that CPT-SSM-VIP is a promising targeted nanomedicine and should be further developed as a safe, long-acting, disease-modifying pharmaceutical product for RA.
Figures
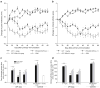
 ) CPT alone. Cumulative areas under the curve were calculated to indicate the relative extents of CIA symptoms. † p< 0.05 CPT-SSM versus SSM; ‡ p<0.05 CPT versus solvent-buffer; § p<0.05 versus normal mice; ¶ p<0.05 CPT-SSM versus CPTalone. N.S. indicates not significantly different (p>0.05). Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (6 mice/group).
) CPT alone. Cumulative areas under the curve were calculated to indicate the relative extents of CIA symptoms. † p< 0.05 CPT-SSM versus SSM; ‡ p<0.05 CPT versus solvent-buffer; § p<0.05 versus normal mice; ¶ p<0.05 CPT-SSM versus CPTalone. N.S. indicates not significantly different (p>0.05). Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (6 mice/group).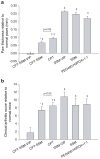

 ) Day 38 and (▮) Day 60. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (6 mice/group). *, † p<0.05 versus SSM-VIP and SSM, respectively.
) Day 38 and (▮) Day 60. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (6 mice/group). *, † p<0.05 versus SSM-VIP and SSM, respectively.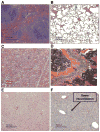
References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–61. - PubMed
-
- Editorial: Painful lessons. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005;12:205. - PubMed
-
- Borchers AT, Keen CL, Cheema GS, Gershwin ME. The use of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004;34:465–83. - PubMed
-
- O’Dell JR. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2591–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

