1H, 13C and 15N NMR assignments of the C1A and C1B subdomains of PKC-delta
- PMID: 21132404
- PMCID: PMC4396712
- DOI: 10.1007/s12104-010-9283-0
1H, 13C and 15N NMR assignments of the C1A and C1B subdomains of PKC-delta
Erratum in
- Biomol NMR Assign. 2013 Apr;7(1):113. Brian, P Ziemba [corrected to Ziemba, Brian P]; Jamie, C Booth [corrected to Booth, Jamie C]; David, Jones N M [corrected to Jones, David N M]
Abstract
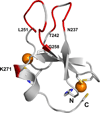
The Protein Kinase C family of enzymes is a group of serine/threonine kinases that play central roles in cell-cycle regulation, development and cancer. A key step in the activation of PKC is translocation to membranes and binding of membrane-associated activators including diacylglycerol (DAG). Interaction of novel and conventional isotypes of PKC with DAG and phorbol esters occurs through the two C1 regulatory domains (C1A and C1B), which exhibit distinct ligand binding selectivity that likely controls enzyme activation by different co-activators. PKC has also been implicated in physiological responses to alcohol consumption and it has been proposed that PKCα (Slater et al. J Biol Chem 272(10):6167-6173, 1997; Slater et al. Biochemistry 43(23):7601-7609, 2004), PKCε (Das et al. Biochem J 421(3):405-413, 2009) and PKCδ (Das et al. J Biol Chem 279(36):37964-37972, 2004; Das et al. Protein Sci 15(9):2107-2119, 2006) contain specific alcohol-binding sites in their C1 domains. We are interested in understanding how ethanol affects signal transduction processes through its affects on the structure and function of the C1 domains of PKC. Here we present the (1)H, (15)N and (13)C NMR chemical shift assignments for the Rattus norvegicus PKCδ C1A and C1B proteins.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mechanism of diacylglycerol-induced membrane targeting and activation of protein kinase Cdelta.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 9;279(28):29501-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403191200. Epub 2004 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15105418
-
Diacylglycerol-induced membrane targeting and activation of protein kinase Cepsilon: mechanistic differences between protein kinases Cdelta and Cepsilon.J Biol Chem. 2005 May 20;280(20):19784-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411285200. Epub 2005 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15769752
-
Activation mechanisms of conventional protein kinase C isoforms are determined by the ligand affinity and conformational flexibility of their C1 domains.J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 21;278(47):46886-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M307853200. Epub 2003 Sep 3. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12954613
-
C1 domains exposed: from diacylglycerol binding to protein-protein interactions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1761(8):827-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.05.001. Epub 2006 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16861033 Review.
-
Indolactam and benzolactam compounds as new medicinal leads with binding selectivity for C1 domains of protein kinase C isozymes.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(12):1371-85. doi: 10.2174/1381612043384907. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15134488 Review.
Cited by
-
Toward a biorelevant structure of protein kinase C bound modulators: design, synthesis, and evaluation of labeled bryostatin analogues for analysis with rotational echo double resonance NMR spectroscopy.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Mar 18;137(10):3678-85. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00886. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25710634 Free PMC article.
-
Structural anatomy of Protein Kinase C C1 domain interactions with diacylglycerol and other agonists.Nat Commun. 2022 May 16;13(1):2695. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30389-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35577811 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of an anesthetic binding site in the second cysteine-rich domain of protein kinase Cδ*.Biophys J. 2012 Dec 5;103(11):2331-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.10.034. Biophys J. 2012. PMID: 23283232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slater SJ, Kelly MB, Larkin JD, Ho C, Mazurek A, Taddeo FJ, Yeager MD, Stubbs CD. Interaction of alcohols and anesthetics with protein kinase Calpha. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:6167–6173. - PubMed
-
- Slater SJ, Malinowski SA, Stubbs CD. The nature of the hydrophobic n-alkanol binding site within the C1 domains of protein kinase Calpha. Biochemistry. 2004;43:7601–7609. - PubMed
-
- Das J, Pany S, Rahman GM, Slater SJ. PKC epsilon has an alcohol-binding site in its second cysteine-rich regulatory domain. Biochem J. 2009;421:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Das J, Addona GH, Sandberg WS, Husain SS, Stehle T, Miller KW. Identification of a general anesthetic binding site in the diacylglycerol-binding domain of protein kinase Cdelta. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:37964–37972. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

