Obstructive airway disease and obstructive sleep apnea: effect of pulmonary function
- PMID: 21132554
- PMCID: PMC3417329
- DOI: 10.1007/s00408-010-9270-3
Obstructive airway disease and obstructive sleep apnea: effect of pulmonary function
Abstract
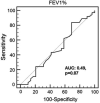
This study sought to determine whether reduced pulmonary function in obstructive airway disease (OAD) is an independent risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This was a prospective observational study conducted at an outpatient pulmonary clinic. Adults with a known diagnosis of COPD/asthma were enrolled as OAD group. Family members without a history of COPD/asthma who accompanied these patients to the clinic were enrolled as a control group. The Berlin Questionnaire (BQ) was used to assess OSA risk in the OAD group and controls. Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV(1) % predicted) was determined from spirometry. The subjects at high risk for OSA were referred for a full overnight polysomnogram (PSG). The prevalence of patients with a high risk of OSA was 55.2% in the OAD group, which was higher than in the controls (7.5%, p < 0.0001). OAD subjects had a higher body mass index (BMI) and larger neck circumference than controls (p < 0.01). There was no difference in FEV(1) % predicted between the OAD patients at high risk and low risk of OSA. On receiver operator curve (ROC) analysis, FEV(1) % predicted was not a significant predictor of high OSA risk. Using logistic regression, FEV(1) % predicted had no association with OSA risk. There was no correlation between FEV(1) % predicted and total apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), oxygen desaturation index, % time spent below oxygen saturation 90%, and mean oxygen saturation on multiple regression analysis. OSA appears to be common in patients with COPD or asthma in an urban outpatient pulmonary clinic. However, the high prevalence of OSA in OAD patients appears to be due to obesity, and reduced pulmonary function is not an independent risk factor for OSA.
Figures
References
-
- Tishler PV, Larkin EK, Schluchter MD, Redline S. Incidence of sleep-disordered breathing in an urban adult population: the relative importance of risk factors in the development of sleep-disordered breathing. JAMA. 2003;289:2230–2237. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1217–1239. - PubMed
-
- Auckley D, Moallem M, Shaman Z, Mustafa M. Findings of a Berlin Questionnaire survey: comparison between patients seen in an asthma clinic versus internal medicine clinic. Sleep Med. 2008;9:494–499. - PubMed
-
- Julien JY, Martin JG, Ernst P, Olivenstein R, Hamid Q, Lemière C, Pepe C, Naor N, Olha A, Kimoff RJ. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea in severe versus moderate asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:371–376. - PubMed