Vitamin D hormone: a multitude of actions potentially influencing the physical function decline in older persons
- PMID: 21134097
- PMCID: PMC4384440
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1447-0594.2010.00668.x
Vitamin D hormone: a multitude of actions potentially influencing the physical function decline in older persons
Abstract
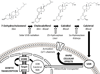
Vitamin D, a secosteroid (pro)-hormone, has been traditionally considered as a key regulator of bone metabolism, and calcium and phosphorous homeostasis through a negative feedback with the parathyroid hormone. However, during the last 20 years, the role played by vitamin D has been largely revised by recognizing its pleiotropic action on a wide spectrum of systems, apparatuses and tissues. Thus, vitamin D has growingly been involved as a primary determinant of biological modifications and specific clinical conditions. The effect of vitamin D on skeletal muscle and related outcomes (including physical function decline and disability) is surely one of the most relevant to study in the context of global aging. In the present review, the subclinical and clinical consequences of vitamin D deficiency/insufficiency, extremely frequent conditions in older age, are described. Special focus is given to skeletal muscle and physical function. Limitations of available scientific evidence on the topic are also discussed.
© 2010 Japan Geriatrics Society.
Figures
References
-
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:266–281. - PubMed
-
- DeLuca HF. Overview of general physiologic features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80:1689S–1696S. - PubMed
-
- Rajakumar K. Vitamin D, cod-liver oil, sunlight, and rickets: a historical perspective. Pediatrics. 2003;112:e132–e135. - PubMed
-
- A dose of vitamin D history. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9:77. - PubMed
-
- Gloth FMr, Gundberg CM, Hollis BW, Haddad JGJ, Tobin JD. Vitamin D deficiency in homebound elderly persons. JAMA. 1995;274:1683–1686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical