Identification of a novel fusion, SQSTM1-ALK, in ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 21134980
- PMCID: PMC3046280
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2010.033514
Identification of a novel fusion, SQSTM1-ALK, in ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
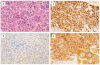
ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma is a rare subtype of lymphoma, and most cases follow an aggressive clinical course with a poor prognosis. We examined an ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma case showing an anti-ALK immunohistochemistry pattern distinct from those of 2 known ALK fusions, CLTC-ALK and NPM-ALK, for the presence of a novel ALK fusion; this led to the identification of SQSTM1-ALK. SQSTM1 is an ubiquitin binding protein that is associated with oxidative stress, cell signaling, and autophagy. We showed transforming activities of SQSTM1-ALK with a focus formation assay and an in vivo tumorigenicity assay using 3T3 fibroblasts infected with a recombinant retrovirus encoding SQSTM1-ALK. ALK-inhibitor therapies are promising for treating ALK-positive large B-cell lymphoma, especially for refractory cases. SQSTM1-ALK may be a rare fusion, but our data provide novel biological insights and serve as a key for the accurate diagnosis of this rare lymphoma.
Figures

References
-
- Delsol G, Lamant L, Mariame B, Pulford K, Dastugue N, Brousset P, et al. A new sub-type of large B-cell lymphoma expressing the ALK kinase and lacking the 2; 5 translocation. Blood. 1997;89(5):1483–90. - PubMed
-
- Laurent C, Do C, Gascoyne RD, Lamant L, Ysebaert L, Laurent G, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a rare clinicopathologic entity with poor prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(25):4211–6. - PubMed
-
- Gascoyne RD, Lamant L, Martin-Subero JI, Lestou VS, Harris NL, Muller-Hermelink HK, et al. ALK-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is associated with Clathrin-ALK rearrangements: report of 6 cases. Blood. 2003;102(7):2568–73. - PubMed
-
- De Paepe P, Baens M, van Krieken H, Verhasselt B, Stul M, Simons A, et al. ALK activation by the CLTC-ALK fusion is a recurrent event in large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2003;102(7):2638–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

