Risk stratification based on both disease status and extra-hematologic comorbidities in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome
- PMID: 21134982
- PMCID: PMC3046276
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2010.033506
Risk stratification based on both disease status and extra-hematologic comorbidities in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome
Abstract
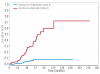
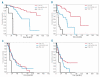
The incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes increases with age and a high prevalence of co-morbid conditions has been reported in these patients. So far, risk assessment in myelodysplastic syndromes has been mainly based on disease status. We studied the prognostic impact of comorbidity on the natural history of myelodysplastic syndrome with the aim of developing novel tools for risk assessment. The study population included a learning cohort of 840 patients diagnosed with myelodysplastic syndrome in Pavia, Italy, and a validation cohort of 504 patients followed in Duesseldorf, Germany. Information on comorbidity was extracted from detailed review of the patients' medical charts and laboratory values at diagnosis and during the course of the disease. Univariable and multivariable survival analyses with both fixed and time-dependent covariates were performed using Cox's proportional hazards regression models. Comorbidity was present in 54% of patients in the learning cohort. Cardiac disease was the most frequent comorbidity and the main cause of non-leukemic death. In multivariable analysis, comorbidity had a significant impact on both non-leukemic death (P=0.01) and overall survival (P=0.02). Cardiac, liver, renal, pulmonary disease and solid tumors were found to independently affect the risk of non-leukemic death. A time-dependent myelodysplastic syndrome-specific comorbidity index (MDS-CI) was developed for predicting the effect of comorbidity on outcome. This identified three groups of patients which showed significantly different probabilities of non-leukemic death (P<0.001) and survival (P=0.005) also in the validation cohort. Landmark survival analyses at fixed time points from diagnosis showed that the MDS-CI can better define the life expectancy of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome stratified according to the WHO-classification based Prognostic Scoring System (WPSS).Comorbidities have a significant impact on the outcome of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Accounting for both disease status by means of the WPSS and comorbidity through the MDS-CI considerably improves risk stratification in myelodysplastic syndromes.
Figures


Comment in
-
Evaluation of overall survival according to myelodysplastic syndrome-specific comorbidity index in a large series of myelodysplastic syndromes.Haematologica. 2011 Oct;96(10):e41-2. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.048991. Haematologica. 2011. PMID: 21972212 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MDS-specific comorbidity index is useful to identify myelodysplastic patients who can have better outcome with 5-azacitidine.Haematologica. 2012 Feb;97(2):e2. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.059808. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 22298822 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cazzola M, Malcovati L. Myelodysplastic syndromes--coping with ineffective hematopoiesis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(6):536–8. - PubMed
-
- Germing U, Strupp C, Kundgen A, Bowen D, Aul C, Haas R, et al. No increase in age-specific incidence of myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica. 2004;89(8):905–10. - PubMed
-
- Rollison DE, Howlader N, Smith MT, Strom SS, Merritt WD, Ries LA, et al. Epidemiology of myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myeloproliferative disorders in the United States, 2001–2004, using data from the NAACCR and SEER programs. Blood. 2008;112(1):45–52. - PubMed
-
- Tefferi A, Vardiman JW. Myelodysplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(19):1872–85. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg SL, Chen E, Corral M, Guo A, Mody-Patel N, Pecora AL, et al. Incidence and clinical complications of myelodysplastic syndromes among United States medicare beneficiaries. J Clin Oncol. 2010 Apr 26;2010 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

