The INO80 ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex is a nucleosome spacing factor
- PMID: 21135121
- PMCID: PMC3028646
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01035-10
The INO80 ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex is a nucleosome spacing factor
Abstract
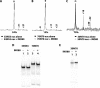
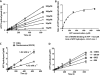
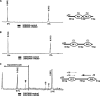
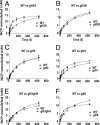
The mobilization of nucleosomes by the ATP-dependent remodeler INO80 is quite different from another remodeler (SWI/SNF) that is also involved in gene activation. Unlike that recently shown for SWI/SNF, INO80 is unable to disassemble nucleosomes when remodeling short nucleosomal arrays. Instead, INO80 more closely resembles, although with notable exceptions, the nucleosome spacing activity of ISW2 and ISW1a, which are generally involved in transcription repression. INO80 required a minimum of 33 to 43 bp of extranucleosomal DNA for mobilizing nucleosomes, with 70 bp being optimal. INO80 prefers to move mononucleosomes to the center of DNA, like ISW2 and ISW1a, but does so with higher precision. Unlike ISW2/1a, INO80 does not require the H4 tail for nucleosome mobilization; instead, the H2A histone tail negatively regulates nucleosome movement by INO80. INO80 moved arrays of two or three nucleosomes with 50 or 79 bp of linker DNA closer together, with a final length of ∼30 bp of linker DNA or a repeat length of ∼177 bp. A minimum length of >30 bp of linker DNA was required for nucleosome movement and spacing by INO80 in arrays.
Figures




References
-
- Bakshi, R., et al. 2004. In silico characterization of the INO80 subfamily of SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 320:197-204. - PubMed
-
- Barbaric, S., et al. 2007. Redundancy of chromatin remodeling pathways for the induction of the yeast PHO5 promoter in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 282:27610-27621. - PubMed
-
- Becker, P. B., and W. Horz. 2002. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:247-273. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, L. A., et al. 2000. Roles of the histone H2A-H2B dimers and the (H3-H4)(2) tetramer in nucleosome remodeling by the SWI-SNF complex. J. Biol. Chem. 275:11545-11552. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
