Locked nucleic acids (LNAs) reveal sequence requirements and kinetics of Xist RNA localization to the X chromosome
- PMID: 21135235
- PMCID: PMC3009817
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1009785107
Locked nucleic acids (LNAs) reveal sequence requirements and kinetics of Xist RNA localization to the X chromosome
Abstract
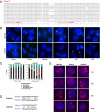
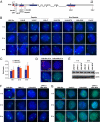
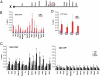
A large fraction of the mammalian genome is transcribed into long noncoding RNAs. The RNAs remain largely uncharacterized as the field awaits new technologies to aid functional analysis. Here, we describe a unique use of locked nucleic acids (LNAs) for studying nuclear long noncoding RNA, an RNA subclass that has been less amenable to traditional knockdown techniques. We target LNAs at Xist RNA and show displacement from the X chromosome with fast kinetics. Xist transcript stability is not affected. By targeting different Xist regions, we identify a localization domain and show that polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) is displaced together with Xist. Thus, PRC2 depends on RNA for both initial targeting to and stable association with chromatin. H3K27-trimethyl marks and gene silencing remain stable. Time-course analysis of RNA relocalization suggests that Xist and PRC2 bind to different regions of the X at the same time but do not reach saturating levels immediately. Thus, LNAs provide a tool for studying an emerging class of regulatory RNA and offer a window of opportunity to target epigenetic modifications with possible therapeutic applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kapranov P, Willingham AT, Gingeras TR. Genome-wide transcription and the implications for genomic organization. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:413–423. - PubMed
-
- Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mattick JS. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Krützfeldt J, et al. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs.’. Nature. 2005;438:685–689. - PubMed
-
- Ørom UA, Kauppinen S, Lund AH. LNA-modified oligonucleotides mediate specific inhibition of microRNA function. Gene. 2006;372:137–141. - PubMed
-
- Morris KV. RNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;320:211–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

