The novel receptor tyrosine kinase Axl is constitutively active in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acts as a docking site of nonreceptor kinases: implications for therapy
- PMID: 21135257
- PMCID: PMC3056640
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-305649
The novel receptor tyrosine kinase Axl is constitutively active in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acts as a docking site of nonreceptor kinases: implications for therapy
Abstract
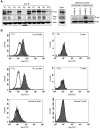
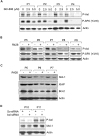
Recently, we detected that chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B-cell-derived microvesicles in CLL plasma carry a constitutively phosphorylated novel receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), Axl, indicating that Axl was acquired from the leukemic B cells. To examine Axl status in CLL, we determined the expression of phosphorylated-Axl (P-Axl) in freshly isolated CLL B cells by Western blot analysis. We detected differential levels of P-Axl in CLL B cells, and further analysis showed that expression of P-Axl was correlated with the other constitutively phosphorylated kinases, including Lyn, phosphoinositide-3 kinase, SyK/ζ-associated protein of 70 kDa, phospholipase C γ2 in CLL B cells. We found that these intracellular signaling molecules were complexed with P-Axl in primary CLL B cells. When Axl and Src kinases were targeted by a Src/Abl kinase inhibitor, bosutinib (SKI-606), or a specific-inhibitor of Axl (R428), robust induction of CLL B-cell apoptosis was observed in both a dose- and time-dependent manner. Therefore, we have identified a novel RTK in CLL B cells which appears to work as a docking site for multiple non-RTKs and drives leukemic cell survival signals. These findings highlight a unique target for CLL treatment.
Figures




References
-
- Pleyer L, Egle A, Hartmann TN, Greil R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of CLL: novel therapeutic approaches. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6(7):405–418. - PubMed
-
- Caligaris-Cappio F. Biology of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2000;4(1):5–21. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411(6835):355–365. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YX, Knyazev PG, Cheburkin YV, et al. AXL is a potential target for therapeutic intervention in breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2008;68(6):1905–1915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

