Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels are specifically associated with memory performance among Alzheimer's disease cases
- PMID: 21135555
- PMCID: PMC3019366
- DOI: 10.1159/000321980
Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels are specifically associated with memory performance among Alzheimer's disease cases
Abstract
Aims: Our purpose was to study the link between serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and neuropsychological functioning through the Texas Alzheimer's Research Consortium cohort.
Methods: A total of 399 participants [probable Alzheimer's disease (AD) n = 198, controls n = 201] were available for analysis. The BDNF levels were assayed via multiplex immunoassay. Regression analyses were utilized to examine the relation between BDNF levels and neuropsychological functioning.
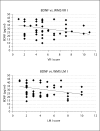
Results: There were no significant mean differences in BDNF levels between cases and controls. In the AD group, the BDNF levels were significantly negatively associated with the scores on immediate [B = -0.07 (0.02), t = -3.55, p = 0.001] and delayed [B = -0.05 (0.02), t = -2.79, p = 0.01] verbal memory and immediate [B = -0.12 (0.05), t = -2.70, p = 0.01] visual memory. No other neuropsychological variables were significantly related to the BDNF levels. The BDNF levels were not significantly related to the neuropsychological test scores in the control group.
Conclusions: Increased serum BDNF levels were associated with poorer visual and verbal memory, but only among AD cases. The current findings point toward an upregulation of serum BDNF as one possible mechanism linked to memory disturbances in AD though it does not appear to be linked to disease severity.
Copyright © 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Tapia-Arancibia L, et al. New insights into brain BDNF function in normal aging and Alzheimer disease. Brain Res Rev. 2008;59:201–220. - PubMed
-
- Kukull WA, et al. Dementia and Alzheimer disease inciden a prospective cohort study. Arch Neurol. 2002;59:1737–1746. - PubMed
-
- Peng S, et al. Precursor form of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor are decreased in the pre-clinical stages of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 2005;93:1412–1421. - PubMed
-
- Holsinger RM, et al. Quantitation of BDNF mRNA in human parietal cortex by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction: decreased levels in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000;76:347–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical