C-peptide microheterogeneity in type 2 diabetes populations
- PMID: 21137020
- PMCID: PMC3761384
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.200800249
C-peptide microheterogeneity in type 2 diabetes populations
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate naturally occurring C-peptide microheterogeneity in healthy and type 2 diabetes (T2D) populations.
Experimental design: MS immunoassays capable of simultaneously detecting intact C-peptide and variant forms were applied to plasma samples from 48 healthy individuals and 48 individuals diagnosed with T2D.
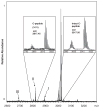
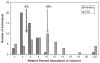
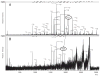
Results: Common throughout the entire sample set were three previously unreported variations of C-peptide. The relative contribution of one variant, subsequently identified as C-peptide (3-31), was found to be more abundant in the T2D population as compared to the healthy population. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV is suspected to be responsible for this particular cleavage product, which is consistent with the pathophysiology of T2D.
Conclusions and clinical relevance: C-peptide does not exist in the human body as a single molecular species. It is qualitatively more heterogeneous than previously thought. These results lay a foundation for future studies devoted to a comprehensive understanding of C-peptide and its variants in healthy and diabetic populations.
Copyright © 2010 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mass spectrometric characterization and activity of zinc-activated proinsulin C-peptide and C-peptide mutants.Analyst. 2010 Feb;135(2):278-88. doi: 10.1039/b917600d. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Analyst. 2010. PMID: 20098759
-
Proteomics-based identification of differentially-expressed proteins including galectin-1 in the blood plasma of type 2 diabetic patients.J Proteome Res. 2009 Mar;8(3):1255-62. doi: 10.1021/pr800850a. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19125585
-
N-terminal segment of proinsulin C-peptide active in insulin interaction/desaggregation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Dec 17;403(3-4):462-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.11.058. Epub 2010 Nov 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 21094141
-
The entero-insular axis: implications for human metabolism.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2008;46(1):43-56. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2008.008. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2008. PMID: 18020966 Review.
-
C-peptide: a molecule balancing insulin states in secretion and diabetes-associated depository conditions.Horm Metab Res. 2013 Oct;45(11):769-73. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1347208. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Horm Metab Res. 2013. PMID: 23780880 Review.
Cited by
-
Mass Spectrometric Immunoassays in Characterization of Clinically Significant Proteoforms.Proteomes. 2016 Mar 17;4(1):13. doi: 10.3390/proteomes4010013. Proteomes. 2016. PMID: 28248223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometric immunoassay of intact insulin and related variants for population proteomics studies.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011 Aug;5(7-8):454-9. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000112. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011. PMID: 21656909 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid development of sensitive, high-throughput, quantitative and highly selective mass spectrometric targeted immunoassays for clinically important proteins in human plasma and serum.Clin Biochem. 2013 Apr;46(6):399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.12.019. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Clin Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23313081 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometric immunoassay revisited.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011 Jun;22(6):960-8. doi: 10.1007/s13361-011-0094-z. Epub 2011 Mar 8. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 21953037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide immunoaffinity enrichment coupled with mass spectrometry for peptide and protein quantification.Clin Lab Med. 2011 Sep;31(3):385-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2011.07.004. Clin Lab Med. 2011. PMID: 21907104 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steiner DF, Clark JL, Nolan C, Rubenstein AH, et al. Proinsulin and the biosynthesis of insulin. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:207–282. - PubMed
-
- Marques RG, Fontaine MJ, Rogers J. C-peptide: much more than a byproduct of insulin biosynthesis. Pancreas. 2004;29:231–238. - PubMed
-
- Chevenne D, Trivin F, Porquet D. Insulin assays and reference values. Diabetes Metab. 1999;25:459–476. - PubMed
-
- Torn C. C-peptide and autoimmune markers in diabetes. Clin Lab. 2003;49:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

