Quercetin induces tumor-selective apoptosis through downregulation of Mcl-1 and activation of Bax
- PMID: 21138867
- PMCID: PMC3069720
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1565
Quercetin induces tumor-selective apoptosis through downregulation of Mcl-1 and activation of Bax
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the in vivo antitumor efficacy of quercetin in U937 xenografts and the functional roles of Mcl-1 and Bax in quercetin-induced apoptosis in human leukemia.
Experimental design: Leukemia cells were treated with quercetin, after which apoptosis, Mcl-1 expression, and Bax activation and translocation were evaluated. The efficacy of quercetin as well as Mcl-1 expression and Bax activation were investigated in xenografts of U937 cells.
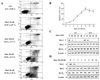
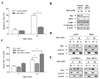
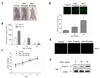
Results: Administration of quercetin caused pronounced apoptosis in both transformed and primary leukemia cells but not in normal blood peripheral mononuclear cells. Quercetin-induced apoptosis was accompanied by Mcl-1 downregulation and Bax conformational change and mitochondrial translocation that triggered cytochrome c release. Knockdown of Bax by siRNA reversed quercetin-induced apoptosis and abrogated the activation of caspase and apoptosis. Ectopic expression of Mcl-1 attenuated quercetin-mediated Bax activation, translocation, and cell death. Conversely, interruption of Mcl-1 by siRNA enhanced Bax activation and translocation, as well as lethality induced by quercetin. However, the absence of Bax had no effect on quercetin-mediated Mcl-1 downregulation. Furthermore, in vivo administration of quercetin attenuated tumor growth in U937 xenografts. The TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells in tumor sections increased in quercetin-treated mice as compared with controls. Mcl-1 downregulation and Bax activation were also observed in xenografts.
Conclusions: These data suggest that quercetin may be useful for the treatment of leukemia by preferentially inducing apoptosis in leukemia versus normal hematopoietic cells through a process involving Mcl-1 downregulation, which, in turn, potentiates Bax activation and mitochondrial translocation, culminating in apoptosis.
©2010 AACR.
Figures



References
-
- Granado-Serrano AB, Martin MA, Bravo L, Goya L, Ramos S. Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-kinase/Akt and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2) J Nutr. 2006;136:2715–2721. - PubMed
-
- van Erk MJ, Roepman P, van der Lende TR, et al. Integrated assessment by multiple gene expression analysis of quercetin bioactivity on anticancer-related mechanisms in colon cancer cells in vitro. Eur J Nutr. 2005;44:143–156. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen TT, Tran E, Nguyen TH, Do PT, Huynh TH, Huynh H. The role of activated MEK-ERK pathway in quercetin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:647–659. - PubMed
-
- Shen SC, Chen YC, Hsu FL, Lee WR. Differential apoptosis-inducing effect of quercetin and its glycosides in human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells by alternative activation of the caspase 3 cascade. J Cell Biochem. 2003;89:1044–1055. - PubMed
-
- Reed JC. Apoptosis-regulating proteins as targets for drug discovery. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7:314–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

