Highly malignant intra-hepatic metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma in rats
- PMID: 21139811
- PMCID: PMC2981431
Highly malignant intra-hepatic metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma in rats
Abstract
Intra-hepatic metastasis is one of the major modalities that lead to the recurrence of advanced HCC. Research efforts to investigate HCC metastasis/recurrence and therapy response will require appropriate models. For our study, the main purpose was to compare two different rodent syngenic orthotopic HCC models using MRI and pathologic evidence; we specifically sought to investigate the intra-hepatic metastatic properties of HCC in Buffalo rats.
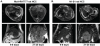
Methods: 12 female Buffalo rats and 16 male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were used in these studies. Subcapsular implantation of 1×10(6) McA-RH7777 and 1×10(6) N1-S1 rat hepatoma cells into the left hepatic lobe was carried out in Buffalo and SD rats, respectively. Buffalo hepatoma rats (n=5/6) and SD hepatoma rats (n=6/8) were imaged using MRI at 6-8 days after implantation. Then, another group of Buffalo HCC rats (n=6/6) and SD HCC (n=6/8) rats were scanned at 21-25 days interval post-implantation. After image acquisition, tumor sections were evaluated with H&E and CD34 staining.
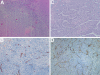
Results: Tumor induction rate for Buffalo rats was 92% (11/12) compared to 75% (12/16) for SD rats. The mean tumor size of McA-RH7777 hepatoma rats at 6-8 day interval was 1.32±0.56cm, but progressed to multiple intra-hepatic metastasis at 21-25 day interval in 6/6 rats (100%). In contrast, the mean tumor size of N1-S1 rats at early interval was 1.06±0.32cm, these progressed to only a single solid mass of 2.35±0.69cm at later interval without obvious intra-hepatic metastasis. H&E staining showed that McA-RH7777 cell induced Morris hepatoma exhibited typical trabecular growth pattern, better representative of human HCC compared to the sheet pattern of N1-S1 cell induced Novikoff hepatoma.
Conclusion: The McA-Rh7777 rat hepatoma model was demonstrated to be a highly malignant intra-hepatic metastasis model of potential utility for HCC research.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); MRI; McARH7777 rat HCC cell line; N1-S1 rat HCC cell line; histopathology; orthotopic implantation; rodent model.
Figures

References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MB, Zhu AX. Hepatocellular carcinoma: the need for progress. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2892–2899. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Alfa GK, Schwartz L, Ricci S, Amadori D, Santoro A, Figer A, De Greve J, Douillard JY, Lathia C, Schwartz B, Taylor I, Moscovici M, Saltz LB. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4293–4300. - PubMed
-
- Maggard M, Meng L, Ke B, Allen R, Devgan L, Imagawa DK. Antisense TGF-beta2 immu-notherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment in a rat tumor model. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001;8:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa T, Tashiro H, Miyata Y, Ushitora Y, Fudaba Y, Kobayashi T, Arihiro K, Okajima M, Asahara T. Rho-associated kinase inhibitor reduces tumor recurrence after liver transplantation in a rat hepatoma model. Am J Transplant. 2007;7:347–355. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
