Antipsychotic occupancy of dopamine receptors in schizophrenia
- PMID: 21143431
- PMCID: PMC6493889
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00222.x
Antipsychotic occupancy of dopamine receptors in schizophrenia
Abstract
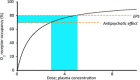
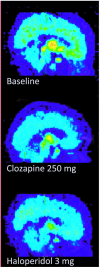
Antipsychotic drugs were introduced in the early 50s on the basis of clinical observations in patients with schizophrenia. Experimental studies later revealed that antagonism at the D(2) dopamine receptor is a common characteristic of all antipsychotic drugs. In the 80s, the advent of brain imaging technologies such as positron emission tomography (PET) allowed for direct noninvasive studies of drug binding in treated patients. The concept receptor occupancy is defined as the fraction (%) of a receptor population that is occupied during treatment with an unlabelled drug. With regard to antipsychotic drugs, the radioligand [(11) C]-raclopride has been the most widely used for binding to the D(2) /D(3) -dopamine receptors. The present review discusses the contribution from molecular imaging to the current understanding of mechanism of action (MoA) of antipsychotic drugs. Consistent initial PET-findings of high D2-receptor occupancy in the striatum of patients responding to different antipsychotic drug treatments provided clinical support for the dopamine hypothesis of antipsychotic drug action. It has subsequently been demonstrated that patients with extrapyramidal syndromes (EPS) have higher occupancy (above 80%) than patients with good response but no EPS (65-80%). The PET-defined interval for optimal antipsychotic drug treatment has been implemented in the evolvement of dose recommendations for classical as well as more recently developed drugs. Another consistent finding is lower D(2) -occupancy during treatment with the prototype atypical antipsychotic clozapine. The MoA of clozapine remains to be fully understood and may include nondopaminergic mechanisms. A general limitation is that currently available PET-radioligands are not selective for any of the five dopamine receptor subtypes. Current attempts at developing such ligands may provide the tools required to refine further the MoA of antipsychotic drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Carlsson A, Lindqvist M. Effect of chlorpromazine or haloperidol on formation of 3‐methoxytyramine and normetanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1963;20:140–144. - PubMed
-
- van Rossum JM. The significance of dopamine‐receptor blockade for the mechanism of action of neuroleptic drugs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1966;160:492–494. - PubMed
-
- Snyder SH. Overview of neurotransmitter receptor binding In: Yamamura HI, editor Neurotransmitter receptor binding New York : Raven Press, 1978;1–11.
-
- Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH. Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science 1976;192:481–483. - PubMed
-
- Seeman P, Lee T, Chau‐Wong M, Wong K. Antipsychotic drug doses and neuroleptic/dopamine receptors. Nature 1976;261:717–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

