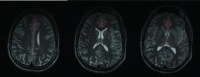
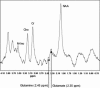
Brain biochemical effects of methylphenidate treatment using proton magnetic spectroscopy in youth with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a controlled pilot study
- PMID: 21143432
- PMCID: PMC4084790
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00226.x
Brain biochemical effects of methylphenidate treatment using proton magnetic spectroscopy in youth with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a controlled pilot study
Abstract
Introduction: This study conducted spectroscopic analyses using proton (1H) Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (at 4 Tesla) in a sample of adolescents with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), before and after treatment with extended release methylphenidate (OROS MPH), as compared to a sample of healthy comparators.
Aims: The main aim of this study is to use 1H MRS to measure differences in brain biochemistry between adolescents with and without ADHD, and to assess changes in cerebral biochemistry, before and after stimulant treatment in ADHD youth.
Results: Subjects with ADHD were medically healthy adolescents treated in an open label fashion with OROS MPH (mean dose: 54 mg/day; 0.90 mg/kg/day). Subjects with ADHD were scanned before and after OROS MPH treatment. Healthy comparators were scanned once. Magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy studies were performed on a 4.0 T Varian Unity/Inova MR scanner; proton spectra were acquired from the Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC). Data were analyzed using MANOVA and repeated measurement ANOVA. Higher metabolite ratios (Glutamate/myo-inositol, Glutamine/myo-inositol, Glutamate + Glutamine/myo-inositol) were observed in the ACC in untreated ADHD subjects as compared to controls, and to treated ADHD youth; these group differences did not reach the a priori threshold for statistical significance.
Conclusions: These preliminary findings suggest the presence of glutamatergic abnormalities in adolescents with ADHD, which may normalize with MPH treatment. Larger sample, controlled studies are needed to confirm these preliminary findings.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00181714.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Carter Petty and Constance Moore report no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pliszka S. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2007;46:894–921. - PubMed
-
- Valera EM, Faraone SV, Murray KE, Seidman LJ. Meta‐analysis of structural imaging findings in attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2007;61:1361–1369. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal N, Port JD, Bazzocchi M, Renshaw PF. Update on the use of MR for assessment and diagnosis of psychiatric diseases. Radiology 2010;255:23–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical