Steroid hormone inactivation is required during the juvenile-adult transition in Drosophila
- PMID: 21145504
- PMCID: PMC3025487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.021
Steroid hormone inactivation is required during the juvenile-adult transition in Drosophila
Abstract
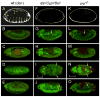
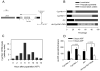
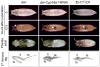
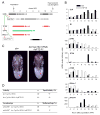
Steroid hormones are systemic signaling molecules that regulate juvenile-adult transitions in both insects and mammals. In insects, pulses of the steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) are generated by increased biosynthesis followed by inactivation/clearance. Although mechanisms that control 20E synthesis have received considerable recent attention, the physiological significance of 20E inactivation remains largely unknown. We show that the cytochrome P450 Cyp18a1 lowers 20E titer during the Drosophila prepupal to pupal transition. Furthermore, this reduction of 20E levels is a prerequisite to induce βFTZ-F1, a key factor in the genetic hierarchy that controls early metamorphosis. Resupplying βFTZ-F1 rescues Cyp18a1-deficient prepupae. Because Cyp18a1 is 20E-inducible, it appears that the increased production of steroid is responsible for its eventual decline, thereby generating the regulatory pulse required for proper temporal progression of metamorphosis. The coupling of hormone clearance to βFTZ-F1 expression suggests a general mechanism by which transient signaling drives unidirectional progression through a multistep process.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CYP18A1, a key enzyme of Drosophila steroid hormone inactivation, is essential for metamorphosis.Dev Biol. 2011 Jan 1;349(1):35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.09.023. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 20932968
-
Juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone coordinately control the developmental timing of matrix metalloproteinase-induced fat body cell dissociation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 29;292(52):21504-21516. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.818880. Epub 2017 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29118190 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila nuclear receptors DHR3 and betaFTZ-F1 control overlapping developmental responses in late embryos.Development. 2010 Jan;137(1):123-31. doi: 10.1242/dev.042036. Development. 2010. PMID: 20023167 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of insect metamorphosis and oogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 May;77(10):1893-1909. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03361-5. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31724082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroid hormone regulation of innate immunity in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Genet. 2023 Jun 15;19(6):e1010782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010782. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37319172 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A dynamical model of growth and maturation in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 5;120(49):e2313224120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2313224120. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38015844 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs involved in Drosophila development and regeneration.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Aug 16;6(3):lqae091. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae091. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39157585 Free PMC article.
-
The Taiman Transcriptional Coactivator Engages Toll Signals to Promote Apoptosis and Intertissue Invasion in Drosophila.Curr Biol. 2019 Sep 9;29(17):2790-2800.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31402304 Free PMC article.
-
Juvenile hormone pathway in honey bee larvae: A source of possible signal molecules for the reproductive behavior of Varroa destructor.Ecol Evol. 2020 Dec 21;11(2):1057-1068. doi: 10.1002/ece3.7125. eCollection 2021 Jan. Ecol Evol. 2020. PMID: 33520186 Free PMC article.
-
The Nutrient-Responsive Hormone CCHamide-2 Controls Growth by Regulating Insulin-like Peptides in the Brain of Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 28;11(5):e1005209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005209. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26020940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andres AJ, Fletcher JC, Karim FD, Thummel CS. Molecular analysis of the initiation of insect metamorphosis: a comparative study of Drosophila ecdysteroid-regulated transcription. Dev Biol. 1993;160:388–404. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner M, Chihara C, Meltzer P, Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. - PubMed
-
- Bassett MH, McCarthy JL, Waterman MR, Sliter TJ. Sequence and developmental expression of Cyp18, a member of a new cytochrome P450 family from Drosophila. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997;131:39–49. - PubMed
-
- Broadus J, McCabe JR, Endrizzi B, Thummel CS, Woodard CT. The Drosophila beta FTZ-F1 orphan nuclear receptor provides competence for stage-specific responses to the steroid hormone ecdysone. Mol Cell. 1999;3:143–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

