T cell cytokines and the risk of blood stream infection in extremely low birth weight infants
- PMID: 21145756
- PMCID: PMC3042892
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2010.11.003
T cell cytokines and the risk of blood stream infection in extremely low birth weight infants
Abstract
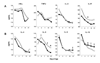
Cytokines mediate the host immune response to infectious micro-organisms. The objective of this study was to determine whether immune regulatory interleukins (IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, and IL-10) and inflammatory cytokines (Interferon-γ [INF-γ], tumor necrosis factor-β [TNF-β], IL-2, and IL-17) are associated with an increased risk of developing blood stream bacterial/fungal infection (BSI) in extremely low birth weight (ELBW) infants. ELBW infants from 17 NICHD Neonatal Research Network centers without early onset sepsis were studied. Cytokines were measured from blood on days 1, 3, 7, 14, and 21 after birth. 996 ELBW infants contributed a minimum of 4080 unique measurements for each cytokine during the five sampling periods. Infants with BSI had lower levels of the inflammatory cytokines IL-17 (p=0.01), and higher levels of the regulatory cytokines, IL-6 (p=0.01) and IL-10 (p<0.001). Higher levels of regulatory cytokines relative to pro-inflammatory cytokines were associated with increased risk of BSI even after adjusting for confounding variables. In ELBW infants, the ratio of immune regulatory cytokines to inflammatory cytokines was associated with development of BSI. Altered maturation of regulatory and inflammatory cytokines may increase the risk of serious infection in this population.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Lemons JA, Donovan EF, Stark AR, Tyson JE, Oh W, Bauer CR, Korones SB, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Stevenson DK, Papile LA, Poole WK. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2002;110:285–291. - PubMed
-
- Bizzarro MJ, Raskind C, Baltimore RS, Gallagher PG. Seventy-five years of neonatal sepsis at Yale: 1928–2003. Pediatrics. 2005;116:595–602. - PubMed
-
- Christensen RD, Rothstein G. Exhaustion of mature marrow neutrophils in neonates with sepsis. J.Pediatr. 1980;96:316–318. - PubMed
-
- Christensen RD, Brown MS, Hall DC, Lassiter HA, Hill HR. Effect on neutrophil kinetics and serum opsonic capacity of intravenous administration of immune globulin to neonates with clinical signs of early-onset sepsis. J.Pediatr. 1991;118:606–614. - PubMed
-
- Schelonka RL, Raaphorst FM, Infante D, Kraig E, Teale JM, Infante AJ. T cell receptor repertoire diversity and clonal expansion in human neonates. Pediatr.Res. 1998;43:396–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 HD27851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD059142/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR6022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR70/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021415/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR7122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR39/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR80/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR16587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR8084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21415/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR997/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- Y1-HD-5000-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR32/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027881/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27881/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

