Disrupted energy metabolism and neuronal circuit dysfunction in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 21147038
- PMCID: PMC3026092
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70277-5
Disrupted energy metabolism and neuronal circuit dysfunction in cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease
Erratum in
- Lancet Neurol. 2011 Feb;10(2):115
Abstract
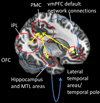
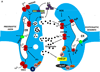
Epidemiological, neuropathological, and functional neuroimaging evidence implicates global and regional disruptions in brain metabolism and energetics in the pathogenesis of cognitive impairment. Nerve cell microcircuits are modified by excitatory and inhibitory synaptic activity and neurotrophic factors. Ageing and Alzheimer's disease cause perturbations in cellular energy metabolism, level of excitation or inhibition, and neurotrophic factor release, which overwhelm compensatory mechanisms and result in dysfunction of neuronal microcircuits and brain networks. A prolonged positive energy balance impairs the ability of neurons to adapt to oxidative and metabolic stress. Results from experimental studies in animals show how disruptions caused by chronic positive energy balance, such as diabetes, lead to accelerated cognitive ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Therapeutic interventions to allay cognitive dysfunction that target energy metabolism and adaptive stress responses (such as neurotrophin signalling) have been effective in animal models and in preliminary studies in humans.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Luchsinger JA, Reitz C, Patel B, et al. Relation of diabetes to mild cognitive impairment. Archives of neurology. 2007;64:570–575. - PubMed
-
- Toro P, Schonknecht P, Schroder J. Type II diabetes in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: results from a prospective population-based study in Germany. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;16:687–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Z01 AG000332/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 AG999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000331/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000327/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000312/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000317/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000975/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000313/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000314/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000313/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000330/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000315/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000312/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

