Interaction of STAT6 with its co-activator SRC-1/NCoA-1 is regulated by dephosphorylation of the latter via PP2A
- PMID: 21148148
- PMCID: PMC3082895
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1225
Interaction of STAT6 with its co-activator SRC-1/NCoA-1 is regulated by dephosphorylation of the latter via PP2A
Abstract
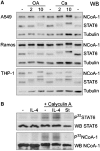
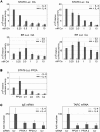
Regulation of gene expression represents a central issue in signal-regulated cellular responses. STAT6 is a critical mediator of IL-4 stimulated gene activation. To mediate this function, STAT6 recruits co-activator complexes. We have previously shown that STAT6 binds the PAS-B domain of the co-activator NCoA-1 via an LXXLL motif in its transactivation domain. Our recent finding that the PAS-B domain of NCoA-1 is also essential for co-activator complex formation points to an additional level of regulation of the co-activator assembly. In this study, we discovered that dephosphorylation of NCoA-1 is essential for the interaction with STAT6 and for IL-4-dependent transcriptional activation. PP2A dephosphorylates NCoA-1 and facilitates the activation of STAT6 target genes. Interestingly, simultaneous inhibition of phosphatase and cyclin-dependent kinases rescues the NCoA-1/STAT6 interaction. Moreover, arrest of cells at G1/S results in enhanced NCoA-1 phosphorylation. In summary, our results indicate that the interaction of NCoA-1 and STAT6 is dynamically regulated by the phosphatase PP2A and by cyclin-dependent kinases. This provides a mechanism for integrating transcriptional regulation by STAT6 with cell cycle progression.
Figures



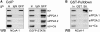


Similar articles
-
An LXXLL motif in the transactivation domain of STAT6 mediates recruitment of NCoA-1/SRC-1.J Biol Chem. 2002 Sep 27;277(39):36052-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203556200. Epub 2002 Jul 22. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12138096
-
Structure of the NCoA-1/SRC-1 PAS-B domain bound to the LXXLL motif of the STAT6 transactivation domain.J Mol Biol. 2004 Feb 13;336(2):319-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.12.057. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14757047
-
P160/SRC/NCoA coactivators form complexes via specific interaction of their PAS-B domain with the CID/AD1 domain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Apr;36(6):1847-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn029. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18267973 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling mechanisms, interaction partners, and target genes of STAT6.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006 Jun;17(3):173-88. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2006.01.004. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006. PMID: 16540365 Review.
-
Regulation of protein kinase cascades by protein phosphatase 2A.Trends Biochem Sci. 1999 May;24(5):186-91. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01375-4. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999. PMID: 10322434 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of progesterone receptor activity by cyclin dependent kinases 1 and 2 occurs in part by phosphorylation of the SRC-1 carboxyl-terminus.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;43(8):1157-67. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.04.009. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21550420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nelms K, Keegan AD, Zamorano J, Ryan JJ, Paul WE. The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999;17:701–738. - PubMed
-
- Bruns HA, Kaplan MH. The role of constitutively active Stat6 in leukemia and lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2006;57:245–253. - PubMed
-
- Hebenstreit D, Wirnsberger G, Horejs-Hoeck J, Duschl A. Signaling mechanisms, interaction partners, and target genes of STAT6. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006;17:173–188. - PubMed
-
- Torchia J, Glass C, Rosenfeld MG. Co-activators and co-repressors in the integration of transcriptional responses. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998;10:373–383. - PubMed
-
- Perissi V, Rosenfeld MG. Controlling nuclear receptors: the circular logic of cofactor cycles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005;6:542–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

