Gain-of-function GPIb ELISA assay for VWF activity in the Zimmerman Program for the Molecular and Clinical Biology of VWD
- PMID: 21148813
- PMCID: PMC3056647
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-08-299016
Gain-of-function GPIb ELISA assay for VWF activity in the Zimmerman Program for the Molecular and Clinical Biology of VWD
Abstract
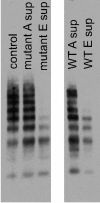
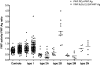
von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a common bleeding disorder, but diagnosis is sometimes challenging because of issues with the current von Willebrand factor (VWF) assays, VWF antigen (VWF:Ag) and VWF ristocetin cofactor activity (VWF:RCo), used for diagnosis. We evaluated 113 healthy controls and 164 VWD subjects enrolled in the T.S. Zimmerman Program for the Molecular and Clinical Biology of VWD for VWF:Ag, VWF:RCo, and a new enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)-based assay of VWF-glycoprotein Ib (GPIb) interactions using a gain-of-function GPIb construct (tGPIbα(235Y;239V)) as a receptor to bind its ligand VWF in an assay independent of ristocetin (VWF:IbCo ELISA). Healthy controls, type 1, 2A, 2M, and 2N subjects had VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratios similar to the ratio obtained with VWF:IbCo ELISA/VWF:Ag. Type 2B VWD subjects, however, had elevated VWF:IbCo ELISA/VWF:Ag ratios. Type 3 VWD subjects had undetectable (< 1.6 U/dL) VWF:IbCo ELISA values. As previously reported, VWF:RCo/VWF:Ag ratio was decreased with a common A1 domain polymorphism, D1472H, as was direct binding to ristocetin for a 1472H A1 loop construct. The VWF:IbCo ELISA, however, was not affected by D1472H. The VWF:IbCo ELISA may be useful in testing VWF binding to GPIb, discrimination of type 2 variants, and in the diagnosis of VWD as it avoids some of the pitfalls of VWF:RCo assays.
Figures




References
-
- Sadler JE, Budde U, Eikenboom JC, et al. Update on the pathophysiology and classification of von Willebrand disease: a report of the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(10):2103–2114. - PubMed
-
- Kitchen S, Jennings I, Woods TA, Kitchen DP, Walker ID, Preston FE. Laboratory tests for measurement of von Willebrand factor show poor agreement among different centers: results from the United Kingdom National External Quality Assessment Scheme for Blood Coagulation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006;32(5):492–498. - PubMed
-
- Meijer P, Haverkate F. An external quality assessment program for von Willebrand factor laboratory analysis: an overview from the European concerted action on thrombosis and disabilities foundation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006;32(5):485–491. - PubMed
-
- Budde U, Pieconka A, Will K, Schneppenheim R. Laboratory testing for von Willebrand disease: contribution of multimer analysis to diagnosis and classification. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2006;32(5):514–521. - PubMed
-
- Favaloro EJ. An update on the von Willebrand factor collagen binding assay: 21 years of age and beyond adolescence but not yet a mature adult. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2007;33(8):727–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

