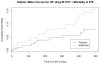
Persistence of cardiovascular risk after rofecoxib discontinuation
- PMID: 21149763
- PMCID: PMC3024905
- DOI: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.461
Persistence of cardiovascular risk after rofecoxib discontinuation
Erratum in
- Arch Intern Med. 2011 Feb 28;171(4):305
Figures
References
-
- Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, et al. Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(11):1092–1102. - PubMed
-
- Baron JA, Sandler RS, Bresalier RS, et al. Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib: final analysis of the APPROVe trial. Lancet. 2008;372(9651):1756–1764. - PubMed
-
- Thal LJ, Ferris SH, Kirby L, et al. A randomized, double-blind, study of rofecoxib in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30(6):1204–1215. - PubMed
-
- Psaty BM, Kronmal RA. Reporting mortality findings in trials of rofecoxib for Alzheimer disease or cognitive impairment: a case study based on documents from rofecoxib litigation. JAMA. 2008;299(15):1813–1817. - PubMed