Evaluation of a glaucoma patient
- PMID: 21150033
- PMCID: PMC3038503
- DOI: 10.4103/0301-4738.73688
Evaluation of a glaucoma patient
Abstract
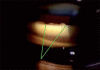
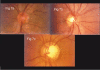
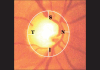
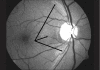
The diagnosis of glaucoma is usually made clinically and requires a comprehensive eye examination, including slit lamp, applanation tonometry, gonioscopy and dilated stereoscopic evaluation of the optic disc and retina. Automated perimetry is obtained if glaucoma is suspected. This establishes the presence of functional damage and provides a baseline for follow-up. Imaging techniques are not essential for the diagnosis but may have a role to play in the follow-up. We recommend a comprehensive eye examination for every clinic patient with the objective of detecting all potentially sight-threatening diseases, including glaucoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

















References
-
- Thomas R, Parikh R, Paul P, Muliyil J. Population-based screening versus case detection. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2002;50:233–7. - PubMed
-
- Grave E, Wienereb R, editors. Hague, Netherlands: Kurger Publication; 2004. Glaucoma Diagnosis: Structure and Function.
-
- San Francisco: CA: American Academy of Ophthalmology; 1996. American Academy of Ophthalmology. Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Preferred Practice Pattern. San Francisco.
-
- SEAGIG Asia Pacific Glaucoma Guidelines. 2nd ed. Available from: http://www.seagig.org[last cited on 2008-09]
-
- Healey P, Thomas R, editors. Oxford UK: Health Press ltd; 2009. The fast facts in glaucoma; pp. 1–128.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

