Anti-malaria drug mefloquine induces motor learning deficits in humans
- PMID: 21151372
- PMCID: PMC2996171
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2010.00191
Anti-malaria drug mefloquine induces motor learning deficits in humans
Abstract
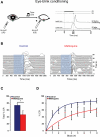
Mefloquine (a marketed anti-malaria drug) prophylaxis has a high risk of causing adverse events. Interestingly, animal studies have shown that mefloquine imposes a major deficit in motor learning skills by affecting the connexin 36 gap junctions of the inferior olive. We were therefore interested in assessing whether mefloquine might induce similar effects in humans. The main aim of this study was to investigate the effect of mefloquine on olivary-related motor performance and motor learning tasks in humans. We subjected nine participants to voluntary motor timing (dart throwing task), perceptual timing (rhythm perceptual task) and reflex timing tasks (eye-blink task) before and 24 h after the intake of mefloquine. The influence of mefloquine on motor learning was assessed by subjecting participants with and without mefloquine intake (controls: n = 11 vs mefloquine: n = 8) to an eye-blink conditioning task. Voluntary motor performance, perceptual timing, and reflex blinking were not affected by mefloquine use. However, the influence of mefloquine on motor learning was substantial; both learning speed as well as learning capacity was impaired by mefloquine use. Our data suggest that mefloquine disturbs motor learning skills. This adverse effect can have clinical as well as social clinical implications for mefloquine users. Therefore, this side-effect of mefloquine should be further investigated and recognized by clinicians.
Keywords: cerebellum; eye-blink conditioning; gap junctions; mefloquine; motor behavior.
Figures



References
-
- Barraud de Lagerie S., Comets E., Gautrand C., Fernandez C., Auchere D., Singlas E., Mentre F., Gimenez F. (2004). Cerebral uptake of mefloquine enantiomers with and without the P-gp inhibitor elacridar (GF1210918) in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 141, 1214–1222 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705721 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baudry S., Pham Y. T., Baune B., Vidrequin S., Crevoisier C., Gimenez F., Farinotti R. (1997). Stereoselective passage of mefloquine through the blood–brain barrier in the rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 49, 1086–1090 - PubMed
-
- Coker S. J., Batey A. J., Lightbown I. D., Diaz M. E., Eisner D. A. (2000). Effects of mefloquine on cardiac contractility and electrical activity in vivo, in isolated cardiac preparations, and in single ventricular myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 129, 323–330 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703060 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

