A quantitative trait locus on chromosome 5p influences d-dimer levels in the san antonio family heart study
- PMID: 21151504
- PMCID: PMC2989697
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/490241
A quantitative trait locus on chromosome 5p influences d-dimer levels in the san antonio family heart study
Abstract
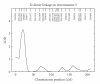
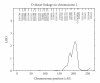
Background. D-dimer is associated with increasing severity of atherosclerosis and with increased risk of a cardiovascular disease (CVD). Methods and Results. To better understand this risk factor, we performed a genome scan on 803 (301 males and 502 females) Mexican Americans in the San Antonio Family Heart Study (SAFHS). The SAFHS is ideal for the discovery of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) influencing CVD because CVD risk factors are prevalent in Mexican Americans of San Antonio and because the study design involves large families, which is optimal for QTL discovery. D-dimer levels were normalized in our study. We found that D-dimer levels were heritable, at about 23% heritability (P ≈ .00001). In a linkage analysis employing 432 microsatellite markers, we found strong evidence of a QTL on chromosome 5p with a lod score of 3.32 at 21 centiMorgans (cM). We also found suggestive evidence of a QTL on chromosome 2q with a lod score of 2.33 at 207 cM. Conclusions. To our knowledge, the putative QTL on chromosome 5p is novel. The possible QTL on chromosome 2q is discussed in relation to a recent report of linkage of a related hemostatic factor to the same location. These results warrant further investigation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A chromosome 11q quantitative-trait locus influences change of blood-pressure measurements over time in Mexican Americans of the San Antonio Family Heart Study.Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Oct;81(4):744-55. doi: 10.1086/521151. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Am J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17846999 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait locus on chromosome 12q14.1 influences variation in plasma plasminogen levels in the San Antonio Family Heart Study.Hum Biol. 2007 Oct;79(5):515-23. doi: 10.1353/hub.2008.0008. Hum Biol. 2007. PMID: 18478967
-
Quantitative trait loci on chromosomes 2p, 4p, and 13q influence bone mineral density of the forearm and hip in Mexican Americans.J Bone Miner Res. 2003 Dec;18(12):2245-52. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.12.2245. J Bone Miner Res. 2003. PMID: 14672361
-
A quantitative trait locus on chromosome 16q influences variation in plasma HDL-C levels in Mexican Americans.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003 Feb 1;23(2):339-45. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000051406.14162.6a. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12588781
-
Two quantitative trait loci affect ACE activities in Mexican-Americans.Hypertension. 2004 Feb;43(2):466-70. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000111830.36999.94. Epub 2004 Jan 5. Hypertension. 2004. PMID: 14707162
Cited by
-
A genetic association study of D-dimer levels with 50K SNPs from a candidate gene chip in four ethnic groups.Thromb Res. 2014 Aug;134(2):462-7. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.05.018. Epub 2014 May 20. Thromb Res. 2014. PMID: 24908450 Free PMC article.
-
D-Dimer in African Americans: Whole Genome Sequence Analysis and Relationship to Cardiovascular Disease Risk in the Jackson Heart Study.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Nov;37(11):2220-2227. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310073. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28912365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sidelmann JJ, Gram J, Jespersen J, Kluft C. Fibrin clot formation and lysis: basic mechanisms. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis. 2000;26(6):605–618. - PubMed
-
- Danesh J, Whincup P, Walker M, et al. Fibrin D-dimer and coronary heart disease prospective study and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2001;103(19):2323–2327. - PubMed
-
- Folsom AR, Aleksic N, Park E, Salomaa V, Juneja H, Wu KK. Prospective study of fibrinolytic factors and incident coronary heart disease: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2001;21(4):611–617. - PubMed
-
- Lowe GDO, Yarnell JWG, Rumley A, Bainton D, Sweetnam PM. C-reactive protein, fibrin d-dimer, and incident ischemic heart disease in the speedwell study: are inflammation and fibrin turnover linked in pathogenesis? Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2001;21(4):603–610. - PubMed
-
- Lowe GDO, Rumley A, McMahon AD, Ford I, O'Reilly DStJ, Packard CJ. Interleukin-6, fibrin D-dimer, and coagulation factors VII and XIIa in prediction of coronary heart disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2004;24(8):1529–1534. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

