Analytical Validation of a Highly Quantitative, Sensitive, Accurate, and Reproducible Assay (HERmark) for the Measurement of HER2 Total Protein and HER2 Homodimers in FFPE Breast Cancer Tumor Specimens
- PMID: 21151530
- PMCID: PMC2990097
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/814176
Analytical Validation of a Highly Quantitative, Sensitive, Accurate, and Reproducible Assay (HERmark) for the Measurement of HER2 Total Protein and HER2 Homodimers in FFPE Breast Cancer Tumor Specimens
Abstract
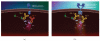
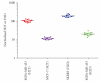
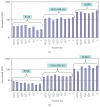
We report here the results of the analytical validation of assays that measure HER2 total protein (H2T) and HER2 homodimer (H2D) expression in Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) breast cancer tumors as well as cell line controls. The assays are based on the VeraTag technology platform and are commercially available through a central CAP-accredited clinical reference laboratory. The accuracy of H2T measurements spans a broad dynamic range (2-3 logs) as evaluated by comparison with cross-validating technologies. The measurement of H2T expression demonstrates a sensitivity that is approximately 7-10 times greater than conventional immunohistochemistry (IHC) (HercepTest). The HERmark assay is a quantitative assay that sensitively and reproducibly measures continuous H2T and H2D protein expression levels and therefore may have the potential to stratify patients more accurately with respect to response to HER2-targeted therapies than current methods which rely on semiquantitative protein measurements (IHC) or on indirect assessments of gene amplification (FISH).
Figures

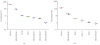



References
-
- Citri A, Skaria KB, Yarden Y. The deaf and the dumb: the biology of ErbB-2 and ErbB-3. Experimental Cell Research. 2003;284(1):54–65. - PubMed
-
- Di Fiore PP, Pierce JH, Kraus MH, Segatto O, King R, Aaronson SA. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987;237(4811):178–182. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2001;2(2):127–137. - PubMed
-
- Hudis CA. Trastuzumab—mechanism of action and use in clinical practice. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2007;357(1):39–51. - PubMed
-
- Ross JS, Slodkowska EA, Symmans WF, Pusztai L, Ravdin PM, Hortobagyi GN. The HER-2 receptor and breast cancer: ten years of targeted anti-HER-2 therapy and personalized medicine. Oncologist. 2009;14(4):320–368. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
