Cystatin C: a candidate biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 21151566
- PMCID: PMC3000338
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015133
Cystatin C: a candidate biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
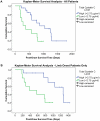
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurologic disease characterized by progressive motor neuron degeneration. Clinical disease management is hindered by both a lengthy diagnostic process and the absence of effective treatments. Reliable panels of diagnostic, surrogate, and prognostic biomarkers are needed to accelerate disease diagnosis and expedite drug development. The cysteine protease inhibitor cystatin C has recently gained interest as a candidate diagnostic biomarker for ALS, but further studies are required to fully characterize its biomarker utility. We used quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to assess initial and longitudinal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma cystatin C levels in 104 ALS patients and controls. Cystatin C levels in ALS patients were significantly elevated in plasma and reduced in CSF compared to healthy controls, but did not differ significantly from neurologic disease controls. In addition, the direction of longitudinal change in CSF cystatin C levels correlated to the rate of ALS disease progression, and initial CSF cystatin C levels were predictive of patient survival, suggesting that cystatin C may function as a surrogate marker of disease progression and survival. These data verify prior results for reduced cystatin C levels in the CSF of ALS patients, identify increased cystatin C levels in the plasma of ALS patients, and reveal correlations between CSF cystatin C levels to both ALS disease progression and patient survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
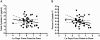
References
-
- Logroscino G, Traynor BJ, Hardiman O, Chio A, Couratier P, et al. Descriptive epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: new evidence and unsolved issues. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008;79:6–11. - PubMed
-
- Louwerse ES, Visser CE, Bossuyt PM, Weverling GJ. Amyotrophiclateral sclerosis: mortality risk during the course of the disease and prognostic factors. The Netherlands ALS Consortium. J Neurol Sci. 1997;152(Suppl 1):S10–17. - PubMed
-
- Testa D, Lovati R, Ferrarini M, Salmoiraghi F, Filippini G. Survival of 793 patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis diagnosed over a 28-year period. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2004;5:208–212. - PubMed
-
- Miller RG, Mitchell JD, Lyon M, Moore DH. Riluzole for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)/motor neuron disease (MND). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD001447. - PubMed
-
- Turner MR, Kiernan MC, Leigh PN, Talbot K. Biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:94–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

