Efficacy and Safety of Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Operation around the Knee to Reduce Adult Height in Extremely Tall Adolescent Girls and Boys
- PMID: 21151661
- PMCID: PMC2997503
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/740629
Efficacy and Safety of Percutaneous Epiphysiodesis Operation around the Knee to Reduce Adult Height in Extremely Tall Adolescent Girls and Boys
Abstract
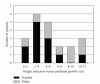
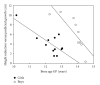
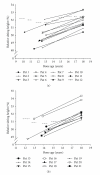
Objective. The aim was to determine efficacy and safety of a surgical method to reduce adult height in extremely tall adolescents. Methods. Data for all girls (n = 12) and boys (n = 9) in our center subjected to bilateral percutaneous epiphysiodesis around the knee who had reached final height were included. Final height predictions were based on hand and wrist X-rays before surgery. Results. When compared to prediction, adult height was reduced by 4.1 ± 0.7 cm in treated girls (P < .001) and 6.4 ± 0.7 cm in treated boys (P < .001) corresponding to a 33.6 ± 3.4% and 33.6 ± 4.2% reduction of remaining growth, respectively. Besides mild to moderate postoperative pain reported in 9 operated individuals, no other side effects were reported. Postoperative X-rays confirmed growth plate closure and absence of leg angulations. Conclusions. Bilateral epiphysiodesis is an effective and safe method to reduce adult height in extremely tall girls and boys.
Figures

References
-
- Simm PJ, Werther GA. Child and adolescent growth disorders–an overview. Australian Family Physician. 2005;34(9):731–737. - PubMed
-
- Verge CF, Mowat D. Overgrowth. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 2010;95(6):458–463. - PubMed
-
- Drop SLS, De Waal WJ, De Muinck Keizer-Schrama SMPF. Sex steroid treatment of constitutionally tall stature. Endocrine Reviews. 1998;19(5):540–558. - PubMed
-
- Venn A, Bruinsma F, Werther PG, et al. Oestrogen treatment to reduce the adult height of tall girls: long-term effects on fertility. The Lancet. 2004;364(9444):1513–1518. - PubMed
-
- Barnard ND, Scialli AR, Bobela S. The current use of estrogens for growth-suppressant therapy in adolescent girls. Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology. 2002;15(1):23–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

