Primary pulmonary plasmacytoma with diffuse alveolar consolidation: a case report
- PMID: 21151727
- PMCID: PMC2990464
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/463465
Primary pulmonary plasmacytoma with diffuse alveolar consolidation: a case report
Abstract
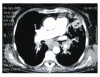
Solitary extramedullary plasmacytomas are plasma cell tumors that tend to develop in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues including the sinonasal or nasopharyngeal regions. Primary plasmacytoma of the lung is exceedingly rare and often presents as a solitary mass or nodule in mid-lung or hilar areas and diagnosed after resection. Herein, we report a case of primary pulmonary plasmacytoma that presented with diffuse alveolar consolidation and diagnosed by transbronchial lung biopsy.
Figures



References
-
- Fletcher C DM. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 3rd edition. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2007.
-
- Horiuchi T, Hirokawa M, Oyama Y, et al. Diffuse pulmonary infiltrates as a roentgenographic manifestation of primary pulmonary plasmacytoma. American Journal of Medicine. 1998;105(1):72–74. - PubMed
-
- Niitsu N, Kohri M, Hayama M, et al. Primary pulmonary plasmacytoma involving bilateral lungs and marked hypergammaglobulinemia: differentiation from extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Leukemia Research. 2005;29(11):1361–1364. - PubMed
-
- Knowles DM, Thompson DD. Neoplastic Hematopathology. 2nd edition. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001.
-
- Koss MN, Hochholzer L, Moran CA, Frizzera G. Pulmonary plasmacytomas: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of five cases. Annals of Diagnostic Pathology. 1998;2(1):1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
