Focal Inflammation Causes Carbenoxolone-Sensitive Tactile Hypersensitivity in Mice
- PMID: 21151805
- PMCID: PMC2999631
- DOI: 10.2174/1876386301003010123
Focal Inflammation Causes Carbenoxolone-Sensitive Tactile Hypersensitivity in Mice
Abstract
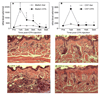
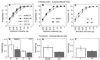
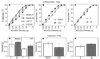
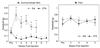
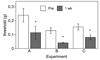
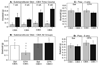
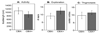
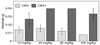
A focal and transitory inflammation induced by injection of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) in the submandibular skin of mice elicits pain behavior that persists for several weeks after the initial inflammation has resolved. Chronic pain, assessed as tactile hypersensitivity to stimulation with von Frey filaments, was evident from 1-7 weeks following CFA injection, although inflammation at the injection site was resolved by 3-4 weeks. In contrast, there were no changes in tactile sensitivity in the paw (un-injected site for comparison), no alterations in open field behavior and no differences in a functional observation battery evident in CFA-treated mice compared to controls (saline-injected) or to baseline (before CFA injection). Neither strain (Balb/c vs. C57BL/6) nor sex differences in baseline tactile threshold were significant in the submandibular skin. CFA-induced tactile hypersensitivity was also not a function of strain or sex. A single intraperitoneal injection of the gap junction blocker carbenoxolone (CBX) restored normal tactile thresholds in CFA-treated mice when administered at the peak of inflammation (1 week), after significant resolution of inflammation (3 weeks) or after total resolution of inflammation (4 and 5 weeks) without altering the tactile threshold of control subjects, tactile threshold in the paw or open field behavior. Thus, in this novel model of post-inflammatory pain, transitory inflammation induced persistent sex- and strain-independent behavioral hypersensitivity that was reversed by the gap junction blocker CBX, suggesting neuronal and/or glial plasticity as a major component of the chronic pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Satellite glial cells in sensory ganglia: their possible contribution to inflammatory pain.Brain Behav Immun. 2007 Jul;21(5):592-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2006.11.011. Epub 2007 Jan 11. Brain Behav Immun. 2007. PMID: 17222529
-
Contribution of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 to chronic pain in aged mice with complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Sep;66(9):2380-90. doi: 10.1002/art.38724. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24891324 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-11 contributes to pain hypersensitivity in the later phase of CFA-induced pain of mice.Brain Res. 2023 Feb 15;1801:148172. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2022.148172. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 36410426
-
The antinociceptive effect of (-)-linalool in models of chronic inflammatory and neuropathic hypersensitivity in mice.J Pain. 2010 Nov;11(11):1222-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.02.022. Epub 2010 May 8. J Pain. 2010. PMID: 20452289
-
Anti-hyperalgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of 4R-tobacco cembranoid in a mouse model of inflammatory pain.J Inflamm (Lond). 2024 Jan 24;21(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12950-023-00373-8. J Inflamm (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38267952 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Subunits 2A and 2B Mediate Connexins and Pannexins in the Trigeminal Ganglion Involved in Orofacial Inflammatory Allodynia during Temporomandibular Joint Inflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):1247-1265. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04291-5. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38976127
-
Broad gap junction blocker carbenoxolone disrupts uterine preparation for embryo implantation in mice.Biol Reprod. 2013 Aug 15;89(2):31. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.113.110106. Print 2013 Aug. Biol Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23843229 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging importance of satellite glia in nervous system function and dysfunction.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Sep;21(9):485-498. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0333-z. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32699292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Air-stimulated ATP release from keratinocytes occurs through connexin hemichannels.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056744. Epub 2013 Feb 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23457608 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Related Changes in Neurons and Satellite Glial Cells in Mouse Dorsal Root Ganglia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 31;24(3):2677. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032677. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lambert GA, Mallos G, Zagami AS. Von Frey's hairs--a review of their technology and use--a novel automated von Frey device for improved testing for hyperalgesia. J Neurosci Methods. 2009;177:420–426. - PubMed
-
- Mulder GB, Pritchett K. Rodent analgesiometry: the hot plate, tail flick and Von Frey hairs. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 2004;43:54–55. - PubMed
-
- Keizer D, van Wijhe M, Post WJ, Wierda JM. Quantifying allodynia in patients suffering from unilateral neuropathic pain using von frey monofilaments. Clin J Pain. 2007;23:85–90. - PubMed
-
- Wolff B. Methods of testing pain mechanism in normal man. In: Wall PD, Melzack R, editors. Textbook of pain. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1984. pp. 186–194.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
