TLR4 inhibits mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) STAT3 activation and thereby exerts deleterious effects on MSC-mediated cardioprotection
- PMID: 21151968
- PMCID: PMC2997048
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014206
TLR4 inhibits mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) STAT3 activation and thereby exerts deleterious effects on MSC-mediated cardioprotection
Abstract
Background: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) improve myocardial recovery after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. These effects are mediated in part by the paracrine secretion of angiogenic and tissue growth-promoting factors. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is expressed by MSC and induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in neuronal progenitors as well as many other cell types. It is unknown whether knock-out (KO) of TLR4 will change the paracrine properties of MSC and in turn improve MSC-associated myocardial protection.
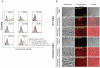
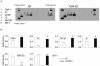
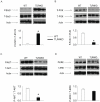
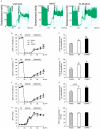
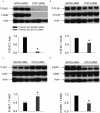
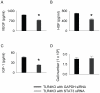
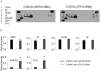
Methodology/principal findings: This study explored the effect of MSC TLR4 on the secretion of angiogenic factors and chemokines in vitro by using ELISA and cytokine array assays and investigated the role of TLR4 on MSC-mediated myocardial recovery after I/R injury in an isolated rat heart model. We observed that MSC isolated from TLR4 KO mice exhibited a greater degree of cardioprotection in a rat model of myocardial I/R injury. This enhanced protection was associated with increased angiogenic factor production, proliferation and differentiation. TLR4-deficiency was also associated with decreased phosphorylation of PI-3K and AKT, but increased activation of STAT3. siRNA targeting of STAT3 resulted in attenuation of the enhanced cardioprotection of TLR4-deficient MSC.
Conclusions/significance: This study indicates that TLR4 exerts deleterious effects on MSC-derived cardioprotection following I/R by a STAT3 inhibitory mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

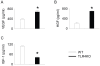
References
-
- Haider H, Ashraf M. Bone marrow stem cell transplantation for cardiac repair. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H2557–2567. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M, Wang Y, Wani MA, Xu M, Ayub A, et al. Implantation of bone marrow stem cells reduces the infarction and fibrosis in ischemic mouse heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35:1113–1119. - PubMed
-
- Gnecchi M, He H, Liang OD, Melo LG, Morello F, et al. Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Med. 2005;11:367–368. - PubMed
-
- Togel F, Hu Z, Weiss K, Isaac J, Lange C, et al. Administered mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischemic acute renal failure through differentiation-independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;289:F31–42. - PubMed
-
- Gnecchi M, He H, Noiseux N, Liang OD, Zhang L, et al. Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. Faseb J. 2006;20:661–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

