NT-proBNP and circulating inflammation markers in prediction of a normal myocardial scintigraphy in patients with symptoms of coronary artery disease
- PMID: 21152016
- PMCID: PMC2995735
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014196
NT-proBNP and circulating inflammation markers in prediction of a normal myocardial scintigraphy in patients with symptoms of coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) can detect myocardial perfusion abnormalities but many examinations are without pathological findings. This study examines whether circulating biomarkers can be used as screening modality prior to MPI.
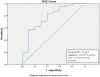
Methodology/principal findings: 243 patients with an intermediate risk of CAD or with known CAD with renewed suspicion of ischemia were referred to MPI. Blood samples were analyzed for N-terminal fragment of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), YKL-40, IL-6, matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and high sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP). Patients with myocardial perfusion defects had elevated levels of NT-proBNP (p<0.0001), YKL-40 (p = 0.03) and IL-6 (p = 0.03) but not of hsCRP (p = 0.58) nor of MMP-9 (p = 0.14). The NT-proBNP increase was observed in both genders (p<0.0001), whereas YKL-40 (p = 0.005) and IL-6 (p = 0.02) were elevated only in men. A NT-proBNP cut off-concentration at 25 ng/l predicted a normal MPI with a negative predictive value >95% regardless of existing CAD.
Conclusions: 20-25% of patients suspected of CAD could have been spared a MPI by using a NT-proBNP cut-off concentration at 25 ng/l with a negative predictive value >95%. NT-proBNP has the potential use of being a screening marker of CAD before referral of the patient to MPI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Coronary Atherosclerosis and Myocardial Ischemia on Plasma Levels of High-Sensitivity Troponin T and NT-proBNP in Patients With Stable Angina.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Apr;36(4):757-64. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306818. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26868212
-
Elevated NT-proBNP and coronary calcium score in relation to coronary artery disease in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients with elevated urinary albumin excretion rate.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Oct;26(10):3242-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr009. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21372253
-
Coronary artery calcium score and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide as potential gatekeepers for myocardial perfusion imaging.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2017 Nov;37(6):710-716. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12363. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27005324
-
Serum YKL-40 predicts long-term mortality in patients with stable coronary disease: a prognostic study within the CLARICOR trial.Immunobiology. 2013 Jul;218(7):945-51. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.10.015. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23294528 Clinical Trial.
-
[N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and ischemia modified albumin (IMA) in exercise induced ischemia in patients with stable coronary artery disease].Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2006 Jul;116(1):640-7. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2006. PMID: 17340970 Polish.
Cited by
-
Almanac 2011: stable coronary artery disease. The national society journals present selected research that has driven recent advances in clinical cardiology.Mater Sociomed. 2011;23(3):129-38. doi: 10.5455/msm.2011.23.129-138. Mater Sociomed. 2011. PMID: 23678298 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prognosis and Reclassification by YKL-40 in Stable Coronary Artery Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Mar 3;9(5):e014634. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014634. Epub 2020 Mar 2. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32114892 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging and C-Reactive Protein in Myocardial Ischemia: A Retrospective Single-Center Study.Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 16;14(2):261. doi: 10.3390/life14020261. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398769 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Serum YKL-40 Level for Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2016 Jan;30(1):23-31. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21804. J Clin Lab Anal. 2016. PMID: 27152377 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium in the prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiac toxicity in children with cancer.J Oncol. 2012;2012:651630. doi: 10.1155/2012/651630. Epub 2012 Oct 16. J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23125858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clark AN, Beller GA. The present role of nuclear cardiology in clinical practice. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;49:43–58. - PubMed
-
- Mowatt G, Vale L, Brazzelli M, Hernandez R, Murray A, et al. Systematic review of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness, and economic evaluation, of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy for the diagnosis and management of angina and myocardial infarction. Health Technol Assess. 2004;8:iii-207. - PubMed
-
- Elhendy A, Schinkel AF, van Domburg RT, Bax JJ, Valkema R, et al. Prognostic value of stress Tc-99m tetrofosmin SPECT in patients with previous myocardial infarction: impact of scintigraphic extent of coronary artery disease. J Nucl Cardiol. 2004;11:704–709. - PubMed
-
- Kroll D, Farah W, McKendall GR, Reinert SE, Johnson LL. Prognostic value of stress-gated Tc-99m sestamibi SPECT after acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2001;87:381–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

