Existing data sources for clinical epidemiology: Aarhus University Prescription Database
- PMID: 21152254
- PMCID: PMC2998817
- DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S13458
Existing data sources for clinical epidemiology: Aarhus University Prescription Database
Abstract
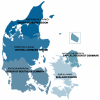
Population-based prescription databases in Nordic countries have become a mainstay of epidemiologic research. Denmark has both national and regional population-based prescription databases. Aarhus University Prescription Database collects data on reimbursed medications dispensed at all community pharmacies of the North Denmark Region and the Central Denmark Region. The regions have a combined population of 1.8 million inhabitants, or one-third of the Danish population. Denmark's primary health care sector, which includes general practitioners, specialists, and dentists, generates about 96% of the prescription sales, most of which are reimbursable and are dispensed by the community pharmacies. The Aarhus University Prescription Database combines the region's pharmacy records in a single database, maintained and updated for research purposes. Each dispensation record contains patient-, drug-, and prescriber-related data. Dispensation records retain patients' universal personal identifier, which allows for individual-level linkage to all Danish registries and medical databases. The linked data have many applications in clinical epidemiology, including drug utilization studies, safety monitoring, etiologic research, and validation studies.
Keywords: epidemiology; prescriptions; registry-based research.
Figures
References
-
- Furu K, Wettermark B, Andersen M, Martikainen JE, Almarsdottir AB, Sørensen HT. The Nordic countries as a cohort for pharmacoepidemiological research. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;106(2):86–94. - PubMed
-
- Hallas J. Conducting pharmacoepidemiologic research in Denmark. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2001;10(7):619–623. - PubMed
-
- Frank L. Epidemiology. The epidemiologist’s dream: Denmark. Science. 2003;301(5630):163. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen GL, Sørensen HT, Pedersen AB, Sabroe S. Analyses of data quality in registries concerning diabetes mellitus – a comparison between a population based hospital discharge and an insulin prescription registry. J Med Syst. 1996;20(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Danish Regions. The Danish regions in brief. 2008. [Accessed 2010 Oct 6]. Available from: http://www.regioner.dk/In%20English/Publications%20and%20Policy%20Papers....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

