Automated Classification of Radiology Reports for Acute Lung Injury: Comparison of Keyword and Machine Learning Based Natural Language Processing Approaches
- PMID: 21152268
- PMCID: PMC2998031
- DOI: 10.1109/BIBMW.2009.5332081
Automated Classification of Radiology Reports for Acute Lung Injury: Comparison of Keyword and Machine Learning Based Natural Language Processing Approaches
Abstract
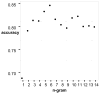
This paper compares the performance of keyword and machine learning-based chest x-ray report classification for Acute Lung Injury (ALI). ALI mortality is approximately 30 percent. High mortality is, in part, a consequence of delayed manual chest x-ray classification. An automated system could reduce the time to recognize ALI and lead to reductions in mortality. For our study, 96 and 857 chest x-ray reports in two corpora were labeled by domain experts for ALI. We developed a keyword and a Maximum Entropy-based classification system. Word unigram and character n-grams provided the features for the machine learning system. The Maximum Entropy algorithm with character 6-gram achieved the highest performance (Recall=0.91, Precision=0.90 and F-measure=0.91) on the 857-report corpus. This study has shown that for the classification of ALI chest x-ray reports, the machine learning approach is superior to the keyword based system and achieves comparable results to highest performing physician annotators.
Figures
References
-
- Chapman WW, Bridewell W, Hanbury P, Cooper GF, Buchanan BG. A simple algorithm for identifying negated findings and diseases in discharge summaries. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2001;34:301–310. - PubMed
-
- NegEx, Negation identification for clinical conditions. Retrieved August 01, 2009, from http://code.google.com/p/negex.
-
- Ratnaparkhi A. IRCS Reports 97—08. University of Pennsylvania; 1997. A simple introduction to Maximum Entropy models for Natural language Processing.
-
- MALLET, Machine Learning for Language Toolkit. Retrieved August 02, 2009, from http://mallet.cs.umass.edu/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources