Pharmacological properties of the ethanol extract of Muehlenbeckia platyclada (F. Muell.) meisn. leaves
- PMID: 21152311
- PMCID: PMC2996782
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms11103942
Pharmacological properties of the ethanol extract of Muehlenbeckia platyclada (F. Muell.) meisn. leaves
Abstract
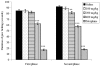
Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of the Muehlenbeckia platyclada leaves' ethanol extract were investigated in animal models. The extract (p.o.) reduced the number of abdominal contortions induced by acetic acid by 21.57% (400 mg/kg). After intraplantar injection of formalin, a dose of 400 mg/kg (p.o.) inhibited the time spent paw licking in the first phase (26.43%), while the second phase was inhibited by 10.90 and 36.65% at the doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg, respectively. The extract (p.o.) increased the reaction time on a hot plate at a dose of 400 mg/kg (32.68 and 40.30%) after 60 and 90 minutes of treatment, respectively. The paw edema was reduced by extract (p.o.) at doses of 100 (15.46 and 16.67%), 200 (22.68 and 25.64%) and 400 mg/kg (29.50 and 37.33%) after 3 to 4 h of carrageenan application, respectively. Doses of 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg (p.o.), administered 4 h after the carrageenan injection, reduced the exudate volume (11.28, 21.54 and 45.13%), while leukocyte migration was reduced by 21.21 and 29.70% at the doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg, respectively. These results indicate that the ethanol extract from M. platyclada may constitute a potential target for the discovery of new molecules with antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities that can be explored for their therapeutic use.
Keywords: Muehlenbeckia platyclada; Polygonaceae; anti-inflammatory activity; antinociceptive activity.
Figures
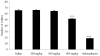
References
-
- Kamboj VP. Herbal medicine. Curr. Sci. 2000;78:35–39.
-
- Patwardhan B, Vaidya ADB, Chorghade M. Ayurved and natural products drug discovery. Curr. Sci. 2004;86:789–799.
-
- Zakaria ZA, Patahuddin H, Mohamad AS, Israf DA, Sulaiman MR. In vivo anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of the aqueous extract of the leaves of Piper sarmentosum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010;128:42–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

