Determination of the thermodegradation of deoxyArbutin in aqueous solution by high performance liquid chromatography
- PMID: 21152314
- PMCID: PMC2996804
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms11103977
Determination of the thermodegradation of deoxyArbutin in aqueous solution by high performance liquid chromatography
Abstract
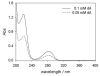
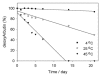
Tyrosinase is the key and rate-limiting enzyme responsible for the conversion of tyrosine into melanin. Competitive inhibition of tyrosinase enzymatic activity results in decreased or absent melanin synthesis by melanocytes in human skin. DeoxyArbutin (4-[(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy]phenol), a novel skin whitening agent, was synthesized through the removal of hydroxyl groups from the glucose side-chain of arbutin. DeoxyArbutin not only shows greater inhibition of tyrosinase activity but is also safer than hydroquinone and arbutin. Hence, deoxyArbutin is a potential skin whitening agent for cosmetics and depigmenting drugs; however, stability of this compound under some conditions remains a problem. The lack of stability poses developmental and practical difficulties for the use of deoxyArbutin in cosmetics and medicines. Improving the thermostability of deoxyArbutin is an important issue for its development. In this research, we established an analytical procedure to verify the amount of deoxyArbutin in solutions using a high performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method. The results indicate that this novel skin whitening agent is a thermolabile compound in aqueous solutions. Additionally, the rate constant for thermodegradation (k) and the half-life (t(1/2)) of deoxyArbutin were determined and can be used to understand the thermodegradation kinetics of deoxyArbutin. This information can aid in the application of deoxyArbutin for many future uses.
Keywords: deoxyArbutin; hydroquinone; skin whitening; thermostability; tyrosinase inhibitor.
Figures
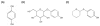



References
-
- Costin GE, Hearing VJ. Human skin pigmentation: Melanocytes modulate skin color in response to stress. Faseb. J. 2007;21:976–994. - PubMed
-
- Lee J, Jung K, Kim YS, Park D. Diosgenin inhibits melanogenesis through the activation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway (PI3K) signaling. Life Sci. 2007;81:249–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

