Stability and folding behavior analysis of zinc-finger using simple models
- PMID: 21152317
- PMCID: PMC2996801
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms11104014
Stability and folding behavior analysis of zinc-finger using simple models
Abstract
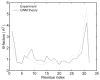
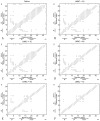
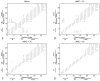
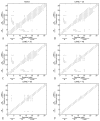
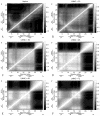
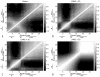
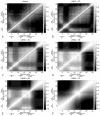
Zinc-fingers play crucial roles in regulating gene expression and mediating protein-protein interactions. In this article, two different proteins (Sp1f2 and FSD-1) are investigated using the Gaussian network model and anisotropy elastic network model. By using these simple coarse-grained methods, we analyze the structural stabilization and establish the unfolding pathway of the two different proteins, in good agreement with related experimental and molecular dynamics simulation data. From the analysis, it is also found that the folding process of the zinc-finger motif is predominated by several factors. Both the zinc ion and C-terminal loop affect the folding pathway of the zinc-finger motif. Knowledge about the stability and folding behavior of zinc-fingers may help in understanding the folding mechanisms of the zinc-finger motif and in designing new zinc-fingers. Meanwhile, these simple coarse-grained analyses can be used as a general and quick method for mechanistic studies of metalloproteins.
Keywords: FSD-1; Gaussian network model; Sp1f2; anisotropy elastic network model; folding pathway; zinc finger.
Figures


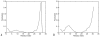

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

